The Root of the Matter: Agroforestry's Impact on Soil Health
Discover the profound impact of agroforestry on soil health and fertility. This informative and inspiring blog post explores how agroforestry practices improve soil structure, enhance nutrient cycling, prevent erosion, and promote long-term sustainability. Join us as we delve into the symbiotic relationship between trees, crops, and soil, and uncover the transformative power of agroforestry in nurturing healthy and resilient soils.

Introduction:
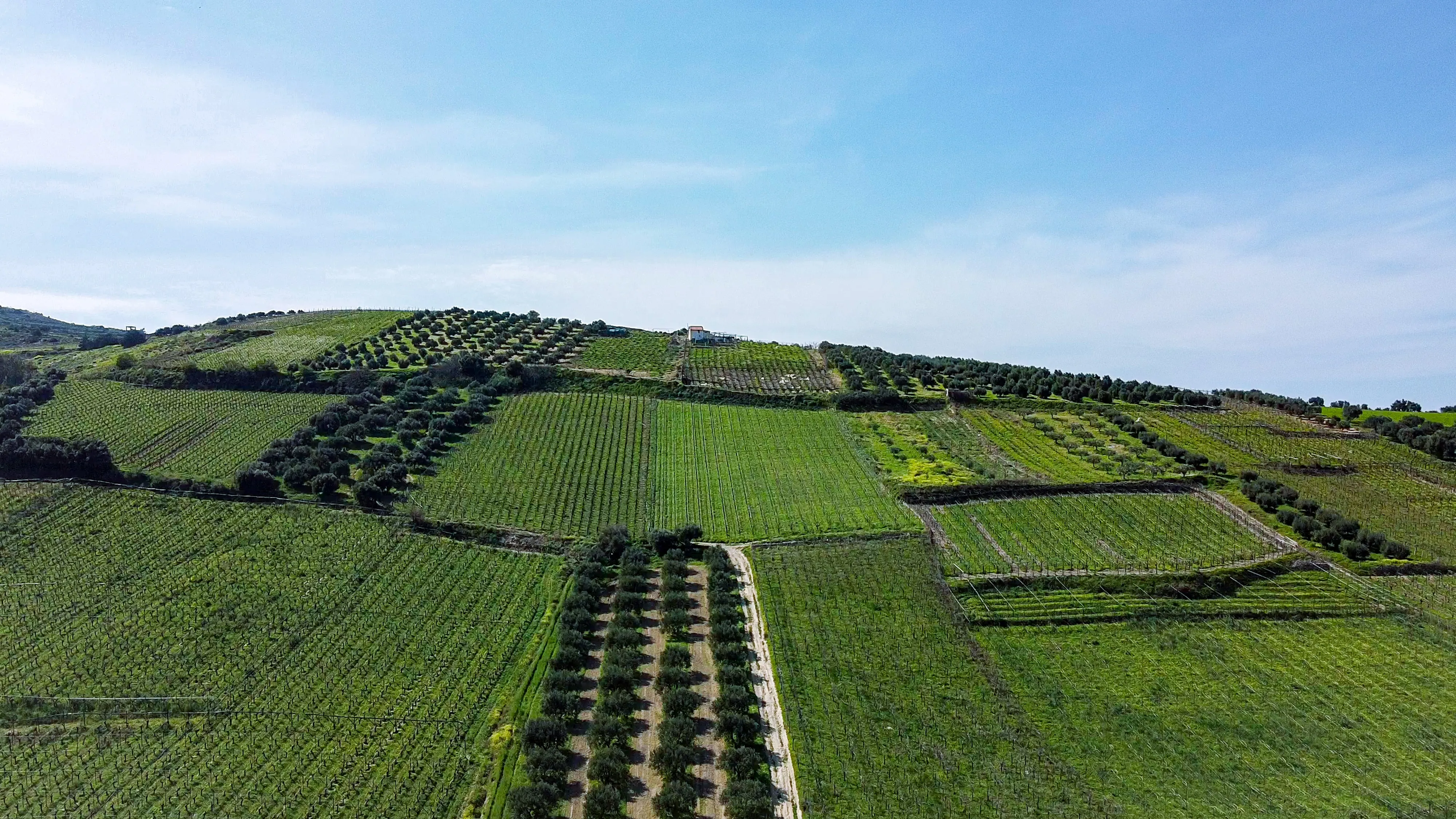
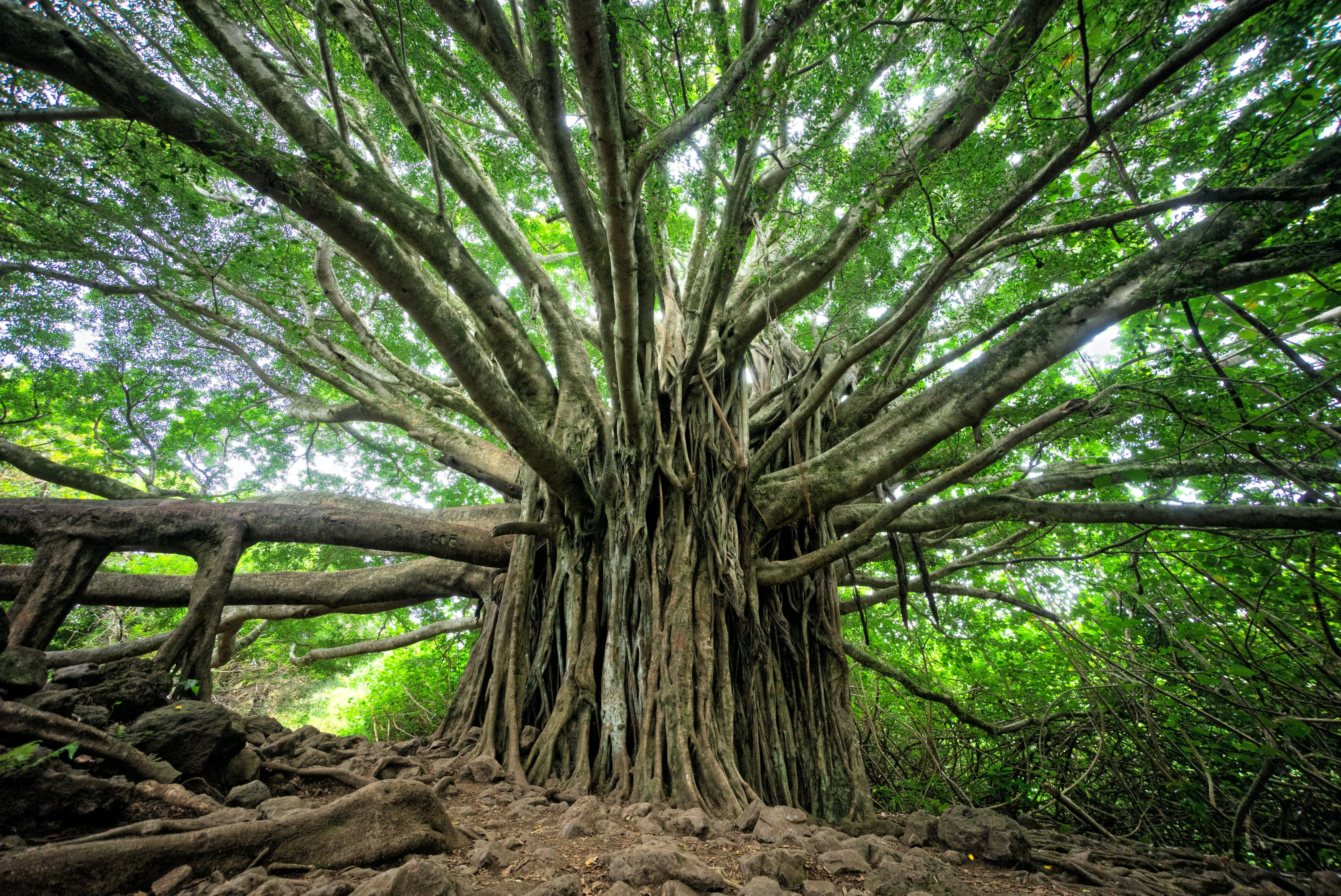
At the heart of every thriving ecosystem lies healthy soil. In the realm of agroforestry, the symbiotic relationship between trees, crops, and soil takes center stage. This blog post uncovers the profound impact of agroforestry on soil health, highlighting the numerous ways in which this integrated land-use system promotes soil fertility, structure, and long-term sustainability. Join us as we explore the intricate connections between agroforestry and soil health, and witness the transformative power of this holistic approach in nurturing healthy and resilient soils.
1. Enhancing Soil Structure:
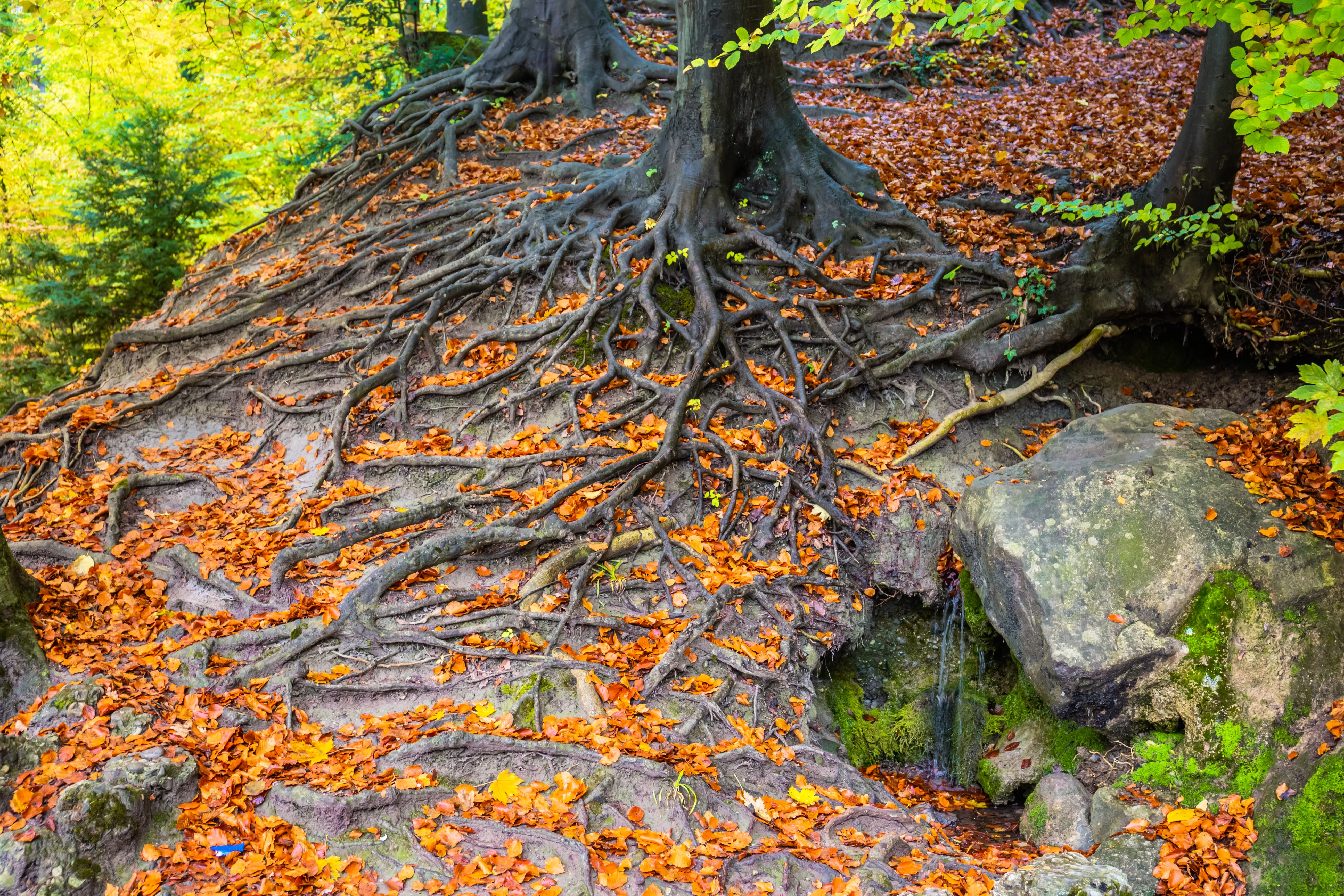
a) Soil Aggregation: Explore how agroforestry practices improve soil structure by enhancing soil aggregation. The presence of trees and their deep-rooted systems create channels for water infiltration, promote aeration, and improve the soil's ability to hold nutrients.
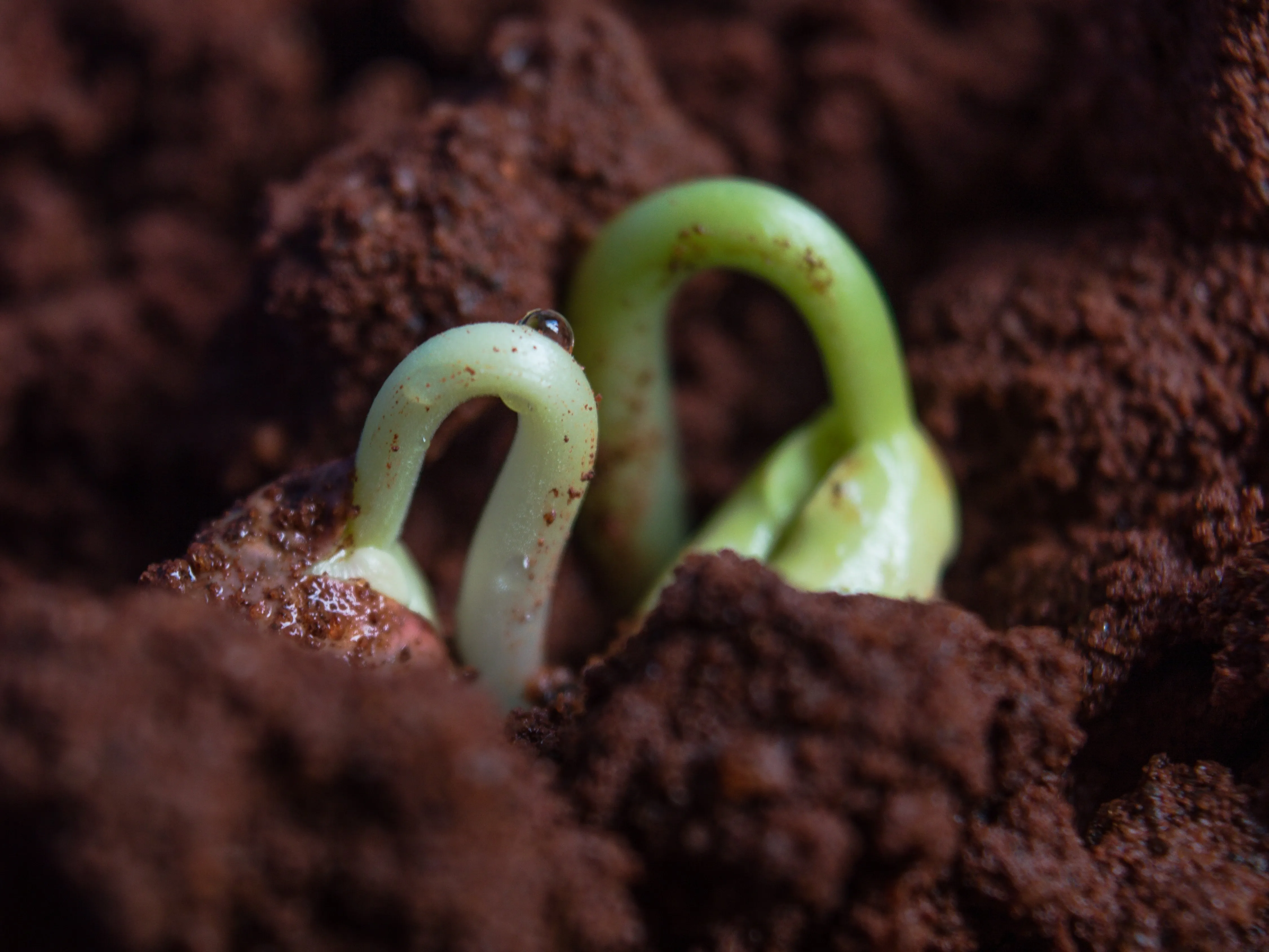
b) Organic Matter Accumulation: Discover how agroforestry systems contribute to organic matter accumulation in the soil. Fallen leaves, branches, and other organic materials from trees enrich the soil, increasing its nutrient content and fostering a thriving microbial community.
2. Nutrient Cycling and Fertilization:
a) Nitrogen Fixation: Learn how agroforestry systems, particularly those involving nitrogen-fixing tree species, enhance nutrient availability through biological nitrogen fixation. These trees capture atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a form that can be utilized by other plants, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
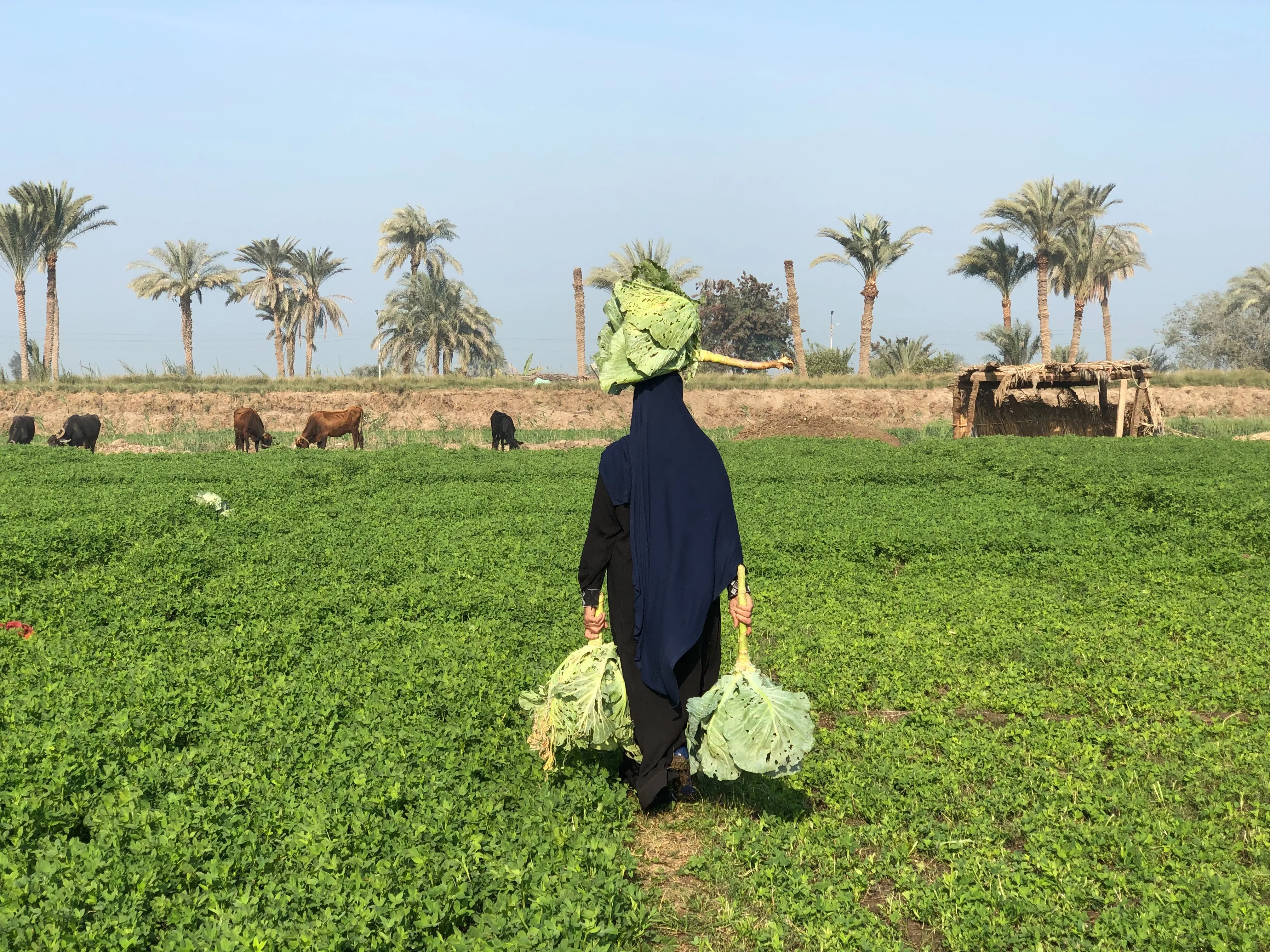
b) Nutrient Cycling: Explore how agroforestry facilitates nutrient cycling within the system. Tree roots scavenge nutrients from deep soil layers and bring them to the surface, benefiting neighboring crops. Additionally, leaf litter and pruned branches serve as natural fertilizers, replenishing the nutrient content of the soil.
3. Soil Erosion Prevention:
a) Soil Stabilization: Discover how agroforestry practices, such as contour planting and windbreaks, help prevent soil erosion. The presence of trees helps to stabilize slopes, reduce surface runoff, and minimize the risk of soil erosion caused by wind and water.
b) Water Infiltration and Retention: Learn how agroforestry systems improve water infiltration and retention in the soil. The leaf canopy and root systems of trees act as natural barriers, allowing water to penetrate the soil and reducing the risk of runoff, thus maximizing water availability for plant uptake.
4. Long-term Sustainability:
a) Soil Conservation: Understand how agroforestry contributes to long-term soil conservation. The integration of trees in agroforestry systems reduces soil degradation and promotes soil fertility, ensuring that the land remains productive for generations to come.
b) Climate Change Resilience: Explore how agroforestry enhances soil resilience in the face of climate change. The shade provided by trees helps moderate soil temperature and moisture levels, reducing the impacts of extreme weather events and enhancing the soil's ability to withstand droughts and floods.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry holds the key to unlocking the potential of healthy and resilient soils. Through its positive impact on soil structure, nutrient cycling, erosion prevention, and long-term sustainability, agroforestry offers a holistic approach to land management that nurtures the very foundation of thriving ecosystems. Let us embrace the power of agroforestry to cultivate healthy soils, ensuring the productivity and sustainability of our land for future generations.