Rewriting the Future: Agroforestry's Role in Sustainable Land Use
Explore the transformative potential of agroforestry in reshaping our future towards sustainable land use. This comprehensive and inspiring blog post delves into the various facets of agroforestry, highlighting its ability to integrate trees, crops, and livestock to optimize land productivity, foster biodiversity, mitigate climate change, and support sustainable livelihoods. Join us as we uncover how agroforestry offers innovative solutions for sustainable land use and a brighter future for generations to come.

Introduction:
As we face mounting environmental challenges and strive for a sustainable future, agroforestry emerges as a beacon of hope. This blog post delves into the transformative potential of agroforestry in reshaping our approach to land use. By integrating trees, crops, and livestock in a synergistic manner, agroforestry presents a holistic solution that optimizes land productivity, fosters biodiversity, mitigates climate change, and supports sustainable livelihoods. Join us on this journey as we explore the diverse benefits of agroforestry and its role in paving the way for sustainable land use practices.
1. Introducing Agroforestry: A Holistic Approach to Land Use
a) Understanding Agroforestry: Learn about the fundamental principles and practices of agroforestry, which involve the intentional integration of trees, crops, and livestock on the same land. This integrated approach allows for the optimization of ecological, economic, and social outcomes.
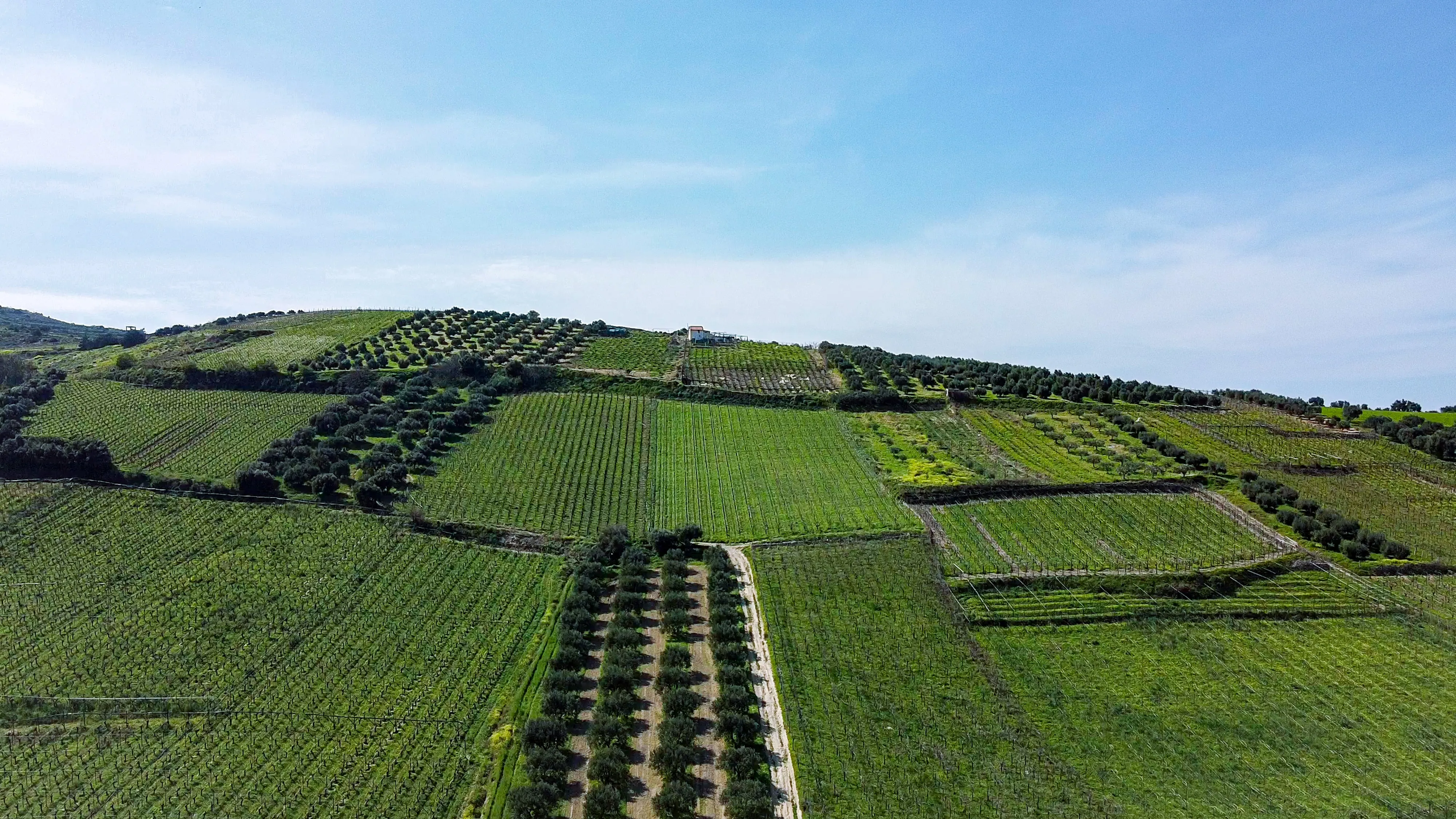
b) Agroforestry Systems: Discover the various types of agroforestry systems, including alley cropping, silvopasture, and forest farming. Each system offers unique benefits and opportunities for sustainable land use, such as increased biodiversity, improved soil health, and diversified income streams.
2. Maximizing Land Productivity: The Power of Agroforestry
a) Ecological Benefits: Explore how the presence of trees in agroforestry systems enhances soil fertility, conserves water, and reduces erosion. Trees provide shade, windbreaks, and habitat for beneficial organisms, resulting in improved crop yields and enhanced land productivity.
b) Crop-Livestock Synergy: Learn how integrating crops and livestock within agroforestry systems creates synergistic relationships. Livestock can benefit from the shade and forage provided by trees, while their manure enriches the soil for crop growth. This integrated approach maximizes land productivity and promotes sustainable resource utilization.
3. Biodiversity Conservation: Nurturing Ecosystem Resilience
a) Habitat Creation: Discover how agroforestry systems act as havens for biodiversity, providing habitat for a variety of plant and animal species. The diverse structure and composition of agroforestry landscapes foster ecological connectivity, helping to restore and conserve biodiversity.
b) Supporting Pollinators: Highlight the crucial role of agroforestry in supporting pollinators such as bees and butterflies. Trees and flowering crops in agroforestry systems provide nectar and pollen sources, promoting pollination services and ensuring the reproductive success of many plant species.
4. Climate Change Mitigation: Agroforestry's Carbon-Sequestering Potential
a) Carbon Sequestration: Explore how trees in agroforestry systems act as powerful carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Agroforestry contributes to climate change mitigation by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable land management practices.
b) Resilience to Climate Change: Learn about the adaptive capacity of agroforestry in the face of climate change. Agroforestry systems offer increased resilience to extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, by regulating water availability and enhancing soil moisture retention.
5. Sustainable Livelihoods: Empowering Communities through Agroforestry
a) Economic Opportunities: Discover the potential economic benefits of agroforestry, including diversified income streams, value-added products, and market opportunities. Agroforestry can support local economies, create employment opportunities, and contribute to sustainable livelihoods for farming communities.
b) Social and Cultural Significance: Recognize the social and cultural importance of agroforestry in preserving traditional knowledge, fostering community engagement, and promoting sustainable land stewardship. Agroforestry practices encourage intergenerational learning and strengthen the social fabric of rural communities.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry offers a transformative pathway to sustainable land use, rewriting the future for generations to come. By integrating trees, crops, and livestock in harmonious systems, agroforestry maximizes land productivity, fosters biodiversity conservation, mitigates climate change, and supports sustainable livelihoods. Embracing agroforestry practices enables us to create resilient and thriving landscapes, where ecological integrity, economic prosperity, and social well-being go hand in hand. Let us embark on this journey together and embrace agroforestry as a cornerstone of sustainable land use practices.