Land Rehabilitation through Agroforestry: Restoring Nature's Harmony
Discover the transformative power of agroforestry in land rehabilitation. This comprehensive blog post explores how agroforestry practices help regenerate degraded lands, prevent soil erosion, restore biodiversity, and provide sustainable livelihoods. Join us as we delve into the inspiring world of land rehabilitation through agroforestry and uncover its potential for creating a harmonious and resilient environment.

Introduction:
In a world grappling with environmental degradation, agroforestry emerges as a powerful tool for land rehabilitation. This blog post delves into the transformative power of agroforestry in restoring degraded lands, preventing soil erosion, revitalizing biodiversity, and fostering sustainable livelihoods. Join us as we explore the inspiring world of land rehabilitation through agroforestry and witness the harmony that emerges when nature and human ingenuity collaborate.
1. Understanding Land Degradation: A Global Challenge
a) The Scope of Land Degradation: Gain insight into the magnitude and consequences of land degradation worldwide. From deforestation to soil erosion and loss of biodiversity, land degradation threatens ecosystems, livelihoods, and the overall health of the planet.
b) The Need for Rehabilitation: Recognize the urgency of land rehabilitation efforts to reverse the effects of degradation. Restoring degraded lands not only supports ecosystem resilience but also provides opportunities for sustainable livelihoods and climate change mitigation.
2. Agroforestry: A Pathway to Land Restoration
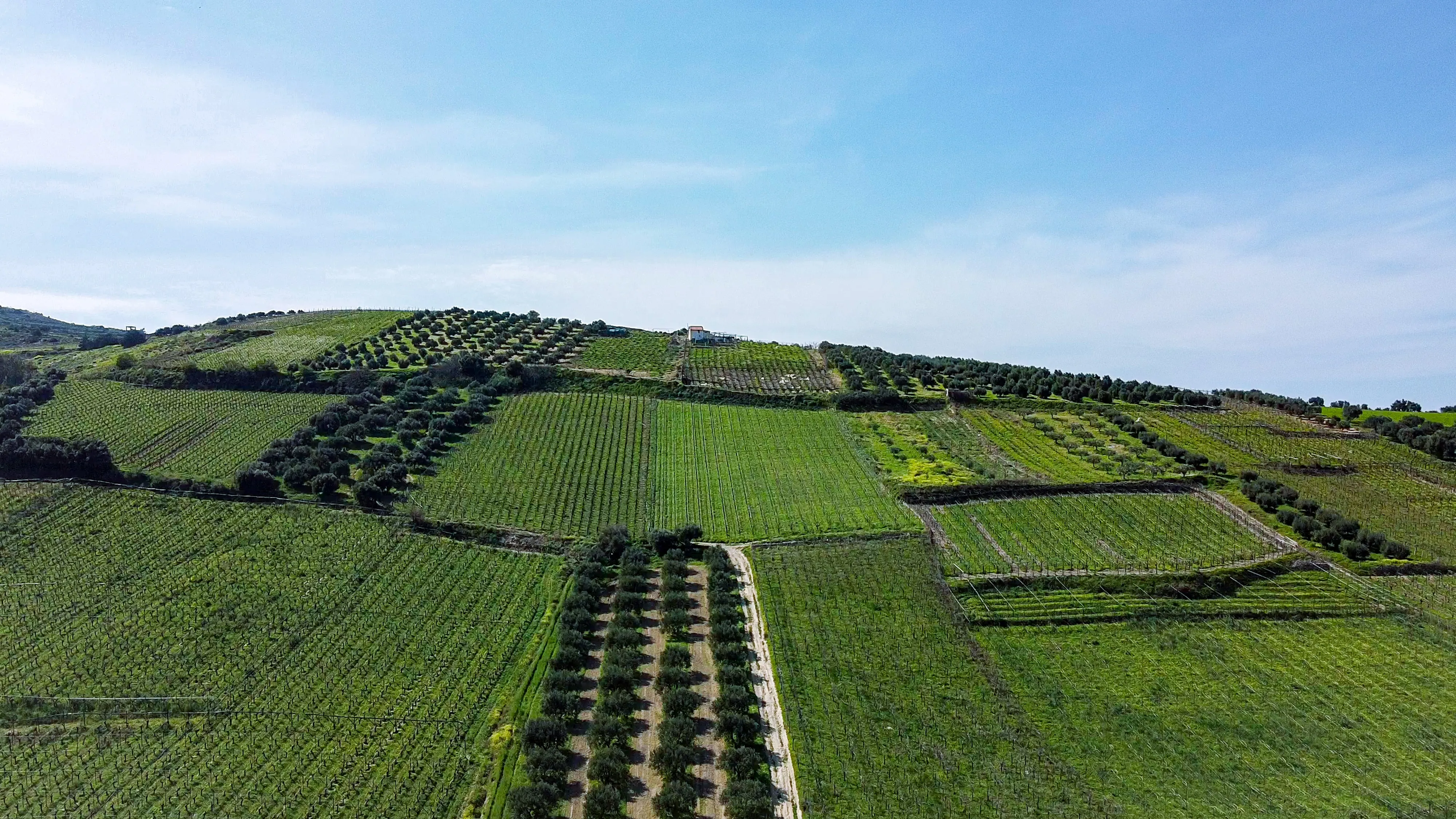
a) The Principles of Agroforestry: Explore the core principles of agroforestry, which combine agriculture and forestry practices in a holistic approach. Agroforestry systems integrate trees, crops, and livestock, creating diverse and sustainable landscapes.
b) Restoring Soil Health: Discover how agroforestry improves soil health and fertility through the introduction of trees. Tree roots enhance soil structure, promote nutrient cycling, and increase water retention capacity, facilitating the recovery of degraded soils.
3. Preventing Soil Erosion: Nature's Protective Shield
a) Tree Windbreaks and Shelterbelts: Learn how strategically planted trees act as windbreaks and shelterbelts, reducing wind speed and preventing soil erosion. These protective barriers stabilize the soil and create microclimates that support agricultural productivity.
b) Contour Planting: Explore the technique of contour planting in agroforestry, which involves planting trees and crops along the contours of the land. This practice helps to slow down water runoff, allowing it to infiltrate the soil and prevent erosion.
4. Restoring Biodiversity: Nurturing Life's Diversity
a) Habitat Creation: Understand how agroforestry systems provide habitat and food sources for a wide range of plant and animal species. The diverse vegetation structure, combined with the presence of trees, attracts beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife, fostering biodiversity.
b) Ecological Corridors: Discover how agroforestry promotes the creation of ecological corridors, connecting fragmented habitats and enabling species movement. These corridors enhance biodiversity by facilitating gene flow, supporting pollination, and improving ecosystem resilience.
5. Sustainable Livelihoods: A Pathway to Prosperity
a) Economic Opportunities: Explore the diverse economic opportunities that arise from agroforestry practices. From timber and non-timber forest products to agroforestry-based enterprises, such as honey production and eco-tourism, agroforestry provides sustainable livelihood options for local communities.
b) Climate Change Resilience: Recognize the role of agroforestry in building climate change resilience. By diversifying income sources and reducing reliance on single crops, agroforestry helps communities adapt to the impacts of climate change and ensures long-term economic stability.
Conclusion:
Land rehabilitation through agroforestry offers a path towards regenerating degraded lands, restoring biodiversity, preventing soil erosion, and creating sustainable livelihoods. Through the harmonious integration of trees, crops, and livestock, agroforestry brings together nature and human ingenuity, resulting in landscapes that are not only productive but also resilient. Let us embrace the transformative potential of agroforestry and work together to restore our lands, foster biodiversity, and create a sustainable future for generations to come.