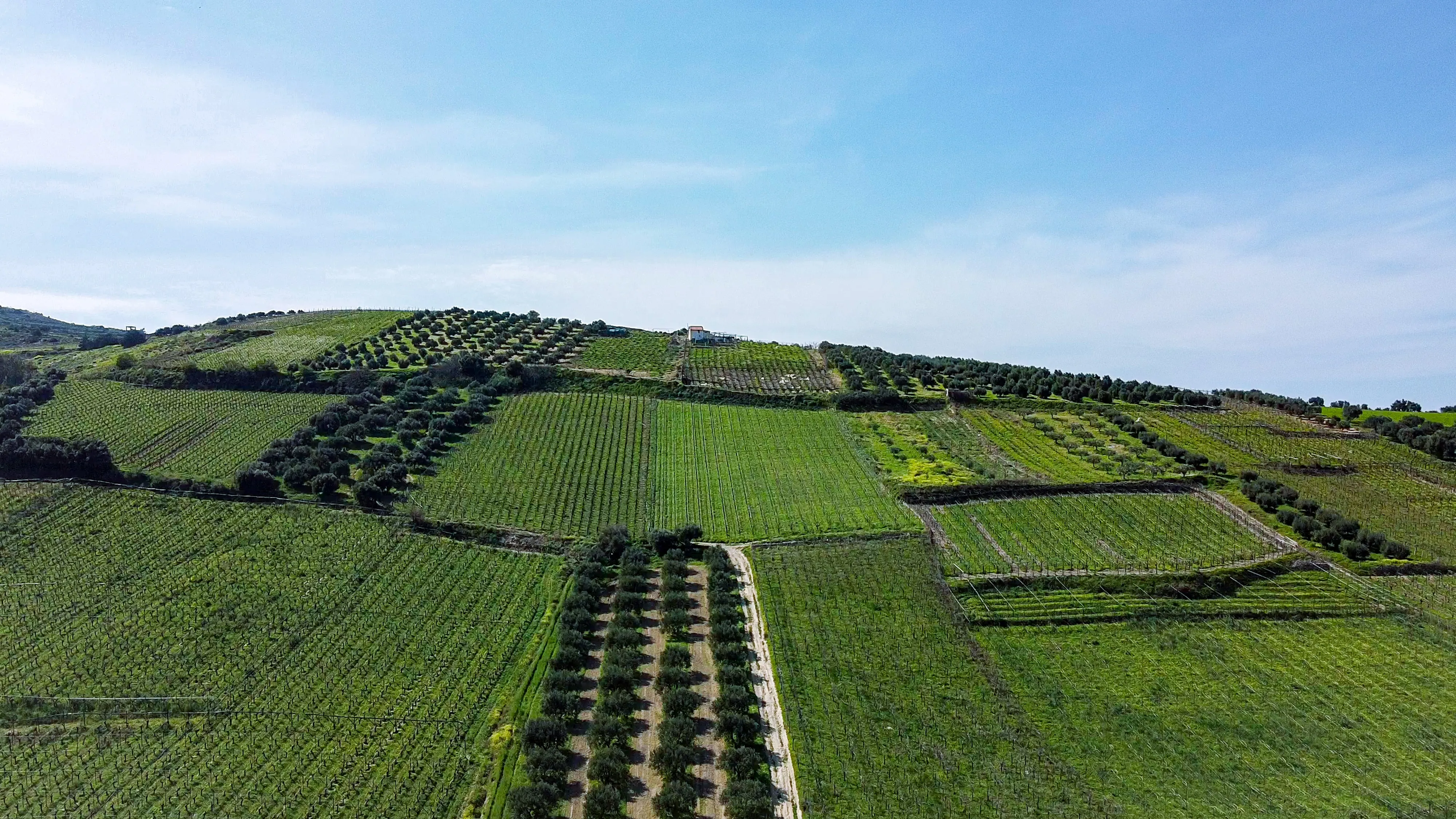
Healing the Land: Agroforestry's Role in Land Rehabilitation
Discover the transformative power of agroforestry in land rehabilitation. This blog post explores how agroforestry practices can heal degraded lands, prevent soil erosion, restore biodiversity, and provide sustainable livelihoods. Join us as we delve into the inspiring world of land rehabilitation through agroforestry and uncover its potential to heal and regenerate our planet.

Introduction:
Land degradation is a pressing global issue that threatens ecosystems, livelihoods, and the overall health of our planet. However, there is hope. Agroforestry, a holistic land management approach that combines agriculture and forestry practices, holds immense promise in rehabilitating degraded lands. In this blog post, we will explore the transformative role of agroforestry in land rehabilitation, highlighting its ability to heal the land, prevent soil erosion, restore biodiversity, and provide sustainable livelihoods. Let's embark on a journey to discover how agroforestry can play a vital role in healing our planet.
1. Understanding Land Degradation:
a) The Global Challenge: Learn about the widespread impacts of land degradation, from deforestation and soil erosion to loss of biodiversity. Understand the urgency of addressing this issue and the consequences it poses for ecosystems and communities worldwide.
b) Land Rehabilitation: Discover why land rehabilitation is crucial for reversing the effects of degradation. Explore the benefits of restoring degraded lands, such as promoting ecosystem resilience, mitigating climate change, and providing sustainable livelihoods for local communities.
2. Agroforestry: A Healing Approach:
a) The Principles of Agroforestry: Gain an understanding of the principles that underpin agroforestry, which combines trees, crops, and livestock in integrated systems. Learn how this approach promotes biodiversity, enhances soil health, and creates resilient landscapes.
b) Restoring Soil Health: Explore how agroforestry practices improve soil health by increasing organic matter, enhancing nutrient cycling, and reducing soil erosion. Discover the role of tree roots in improving soil structure and increasing water infiltration capacity.
3. Preventing Soil Erosion:
a) Windbreaks and Contour Planting: Learn about the use of windbreaks and contour planting in agroforestry to prevent soil erosion. Understand how strategically planted trees act as wind barriers, reducing wind speed and preventing soil loss. Discover how contour planting slows down water runoff, allowing it to infiltrate the soil and prevent erosion.
b) Agroforestry Buffer Strips: Explore the concept of agroforestry buffer strips, which are vegetative strips composed of trees and shrubs. These strips act as protective barriers, reducing sediment runoff and filtering pollutants, thereby preventing soil erosion and improving water quality.
4. Restoring Biodiversity:
a) Habitat Creation: Discover how agroforestry systems provide diverse habitats for a wide range of plant and animal species. Learn how the presence of trees in agroforestry landscapes supports wildlife by providing food, shelter, and nesting sites, ultimately restoring biodiversity.
b) Ecological Connectivity: Understand the importance of ecological connectivity in agroforestry systems. Learn how the interconnectedness of diverse landscapes through agroforestry corridors promotes species movement, gene flow, and pollination, contributing to the restoration of biodiversity.
5. Sustainable Livelihoods:
a) Economic Opportunities: Explore the various economic opportunities that agroforestry provides, such as timber and non-timber forest products, agroforestry-based enterprises, and eco-tourism. Learn how these livelihood options can contribute to the well-being of local communities and foster sustainable development.
b) Community Empowerment: Discover how agroforestry empowers local communities by providing them with sustainable livelihoods, reducing dependency on single crops, and enhancing resilience to climate change. Explore the social and cultural benefits that arise from community involvement in agroforestry initiatives.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry offers a promising solution for land rehabilitation, addressing the challenges of land degradation, soil erosion, biodiversity loss, and sustainable livelihoods. By integrating trees, crops, and livestock, agroforestry promotes ecological restoration, enhances soil health, and provides multiple benefits to communities. Let us embrace the power of agroforestry to heal the land and create a more sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come. Together, we can make a difference and restore the health and vitality of our planet.