From Farm to Fork: Agroforestry's Role in Long-Term Food Security
Explore the vital role of agroforestry in ensuring long-term food security. Discover the benefits of agroforestry investments, including tax savings and the potential for tax-free retirement income. Uncover how agroforestry fosters sustainable farming practices, enhances biodiversity, improves resilience, and secures the future of our food system from farm to fork.

Introduction:
In an ever-changing world, ensuring long-term food security has become a pressing concern. Agroforestry, an innovative and sustainable land management practice, offers a promising solution to this challenge. By integrating trees into agricultural systems, agroforestry provides a multitude of benefits that promote sustainable farming, enhance biodiversity, improve resilience, and secure the future of our food system. This article delves into the transformative role of agroforestry in achieving long-term food security. We will explore the benefits of agroforestry investments, including tax savings and the potential for tax-free retirement income, while highlighting how agroforestry contributes to sustainable agriculture from farm to fork.
1. Understanding Agroforestry:
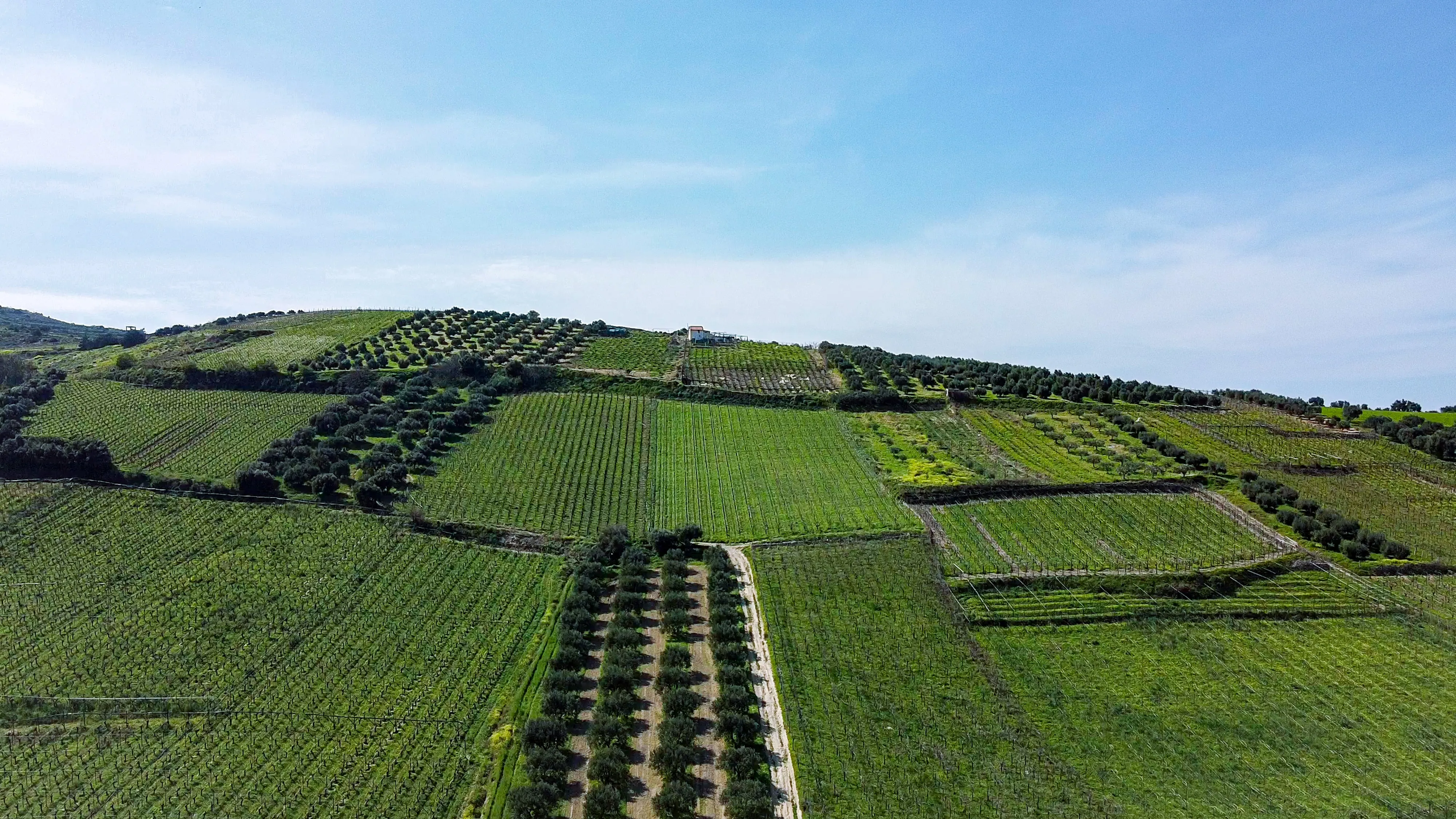
Agroforestry is a holistic approach that combines the cultivation of trees with crops or livestock. It involves the intentional integration of trees within agricultural systems, creating synergistic relationships that bring forth a range of benefits.
2. Sustainable Farming Practices:
a) Enhancing Soil Health: Agroforestry fosters healthy soils by improving soil structure, nutrient cycling, and water retention. The presence of trees in agroforestry systems promotes organic matter accumulation, reduces erosion, and enhances soil fertility, ensuring sustainable and productive farming practices.
b) Diversifying Crops: Agroforestry allows for crop diversification, reducing reliance on a single crop and enhancing resilience against pests, diseases, and market volatility. By integrating diverse crops, agroforestry systems contribute to a more resilient and stable food production system.
3. Biodiversity Conservation:
a) Habitat Creation: Agroforestry systems provide valuable habitats for a diverse range of plant and animal species. The integration of trees supports beneficial insects, pollinators, and wildlife, contributing to enhanced biodiversity within and around agricultural landscapes.
b) Ecological Balance: Agroforestry promotes a balanced ecosystem by attracting natural predators of pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions. This approach reduces the ecological footprint of agriculture and supports the preservation of beneficial species.
4. Climate Resilience:
a) Carbon Sequestration: Agroforestry plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide. Trees in agroforestry systems absorb and store carbon, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
b) Adaptation to Climate Change: Agroforestry enhances the resilience of farming systems to climate change impacts such as extreme weather events and shifting climatic patterns. The presence of trees helps regulate temperature, reduce wind speed, and retain moisture, creating a more favorable microclimate for crops and livestock.
5. Ensuring Food Security:
a) Sustainable and Nutritious Food: Agroforestry promotes the production of diverse and nutritious food. The integration of trees adds variety to the diet, supplying fruits, nuts, and other non-timber forest products alongside traditional crops. This diversification contributes to a more balanced and sustainable food system.
b) Local and Community Resilience: Agroforestry investments strengthen local and community resilience by providing a secure and sustainable food source. By supporting local agriculture, agroforestry helps reduce dependency on external food sources and fosters self-sufficiency within communities.
6. Agroforestry Investments: Securing the Future:
a) Financial Returns: Agroforestry investments offer attractive long-term financial returns. As trees mature, they yield valuable products such as timber, fruits, or medicinal plants, providing a sustainable income stream for investors.
b) Tax Savings and Incentives: Agroforestry investments often come with tax benefits and incentives. Governments recognize the environmental and social advantages of agroforestry and may offer tax deductions or reduced tax rates for agroforestry projects. Leveraging these incentives can lead to significant tax savings for investors.
c) Potential for Tax-Free Retirement Income: Agroforestry investments provide the potential for tax-free retirement income. As trees reach maturity and generate revenue, the income can supplement retirement funds without incurring income tax. This tax-free income provides financial security and stability during retirement.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry plays a crucial role in ensuring long-term food security, fostering sustainable farming practices, enhancing biodiversity, and improving resilience in the face of climate change. Agroforestry investments offer a pathway to secure the future of our food system, providing financial returns, tax savings, and potential tax-free retirement income. By embracing agroforestry, we contribute to sustainable agriculture from farm to fork, ensuring a resilient and secure food supply for generations to come.