From Degradation to Regeneration: The Rehabilitation Potential of Agroforestry
Explore the transformative power of agroforestry in rehabilitating degraded lands. This inspiring blog post delves into the comprehensive benefits of agroforestry, including soil restoration, biodiversity enhancement, climate resilience, and sustainable livelihoods. Discover how agroforestry offers a path from land degradation to regeneration.

Introduction:
The global challenge of land degradation threatens the health of our ecosystems and the well-being of communities around the world. However, amidst this challenge, a beacon of hope emerges in the form of agroforestry. This holistic land management approach combines agriculture and forestry practices to restore degraded lands and regenerate ecosystems. In this blog post, we will embark on a journey to explore the rehabilitation potential of agroforestry, examining its comprehensive benefits in soil restoration, biodiversity enhancement, climate resilience, and the creation of sustainable livelihoods. Join us as we discover how agroforestry can pave the way from degradation to regeneration.
1. Understanding Land Degradation:
a) The Scope of the Problem: Explore the widespread impacts of land degradation, including deforestation, soil erosion, and loss of biodiversity. Understand the urgent need to address this global issue and its implications for environmental and social well-being.
b) The Rehabilitation Imperative: Learn why land rehabilitation is crucial for restoring degraded ecosystems and preserving essential ecosystem services. Discover how agroforestry offers a unique opportunity to reverse the effects of land degradation and foster regeneration.
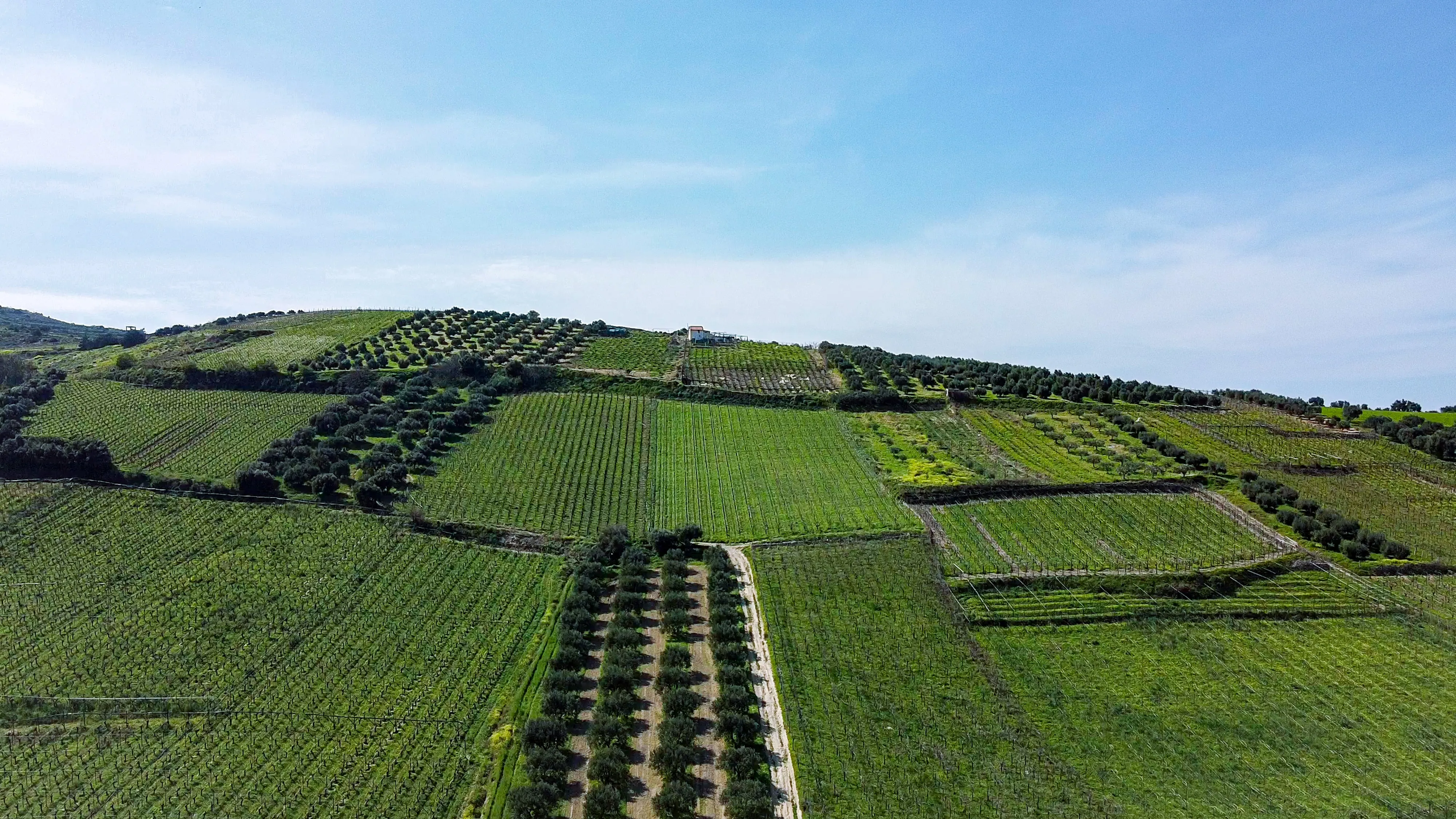
2. Soil Restoration through Agroforestry:
a) Rebuilding Soil Health: Explore how agroforestry practices can rejuvenate degraded soils by increasing organic matter content, improving soil structure, and enhancing nutrient cycling. Understand the role of tree roots in stabilizing soil, reducing erosion, and promoting water infiltration.
b) Soil Erosion Prevention: Discover how agroforestry systems, such as contour planting and agroforestry buffer strips, act as natural shields against soil erosion. Learn how the strategic placement of trees and shrubs helps reduce water runoff, retain sediments, and protect vulnerable soil.
3. Biodiversity Enhancement:
a) Creating Habitat Diversity: Explore how agroforestry systems provide diverse habitats that support a wide range of plant and animal species. Learn how the combination of trees, crops, and livestock creates a mosaic of ecological niches, promoting biodiversity conservation.
b) Ecological Corridors: Discover how agroforestry can facilitate the establishment of ecological corridors, connecting fragmented habitats and enabling the movement of species. Understand the importance of these corridors in maintaining genetic diversity, facilitating pollination, and fostering ecosystem resilience.
4. Climate Resilience and Carbon Sequestration:
a) Mitigating Climate Change: Learn how agroforestry helps mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide through the growth and development of trees. Explore the potential of agroforestry systems to serve as carbon sinks, contributing to global efforts in climate change adaptation and mitigation.
b) Enhancing Resilience: Understand how agroforestry systems enhance the resilience of ecosystems and communities by diversifying income streams, providing shade and shelter, conserving water resources, and protecting against extreme weather events.
5. Sustainable Livelihoods:
a) Economic Opportunities: Discover the diverse economic opportunities that agroforestry offers, including timber and non-timber forest products, agroforestry-based enterprises, and eco-tourism. Learn how these livelihood options can generate income, promote local entrepreneurship, and improve community well-being.
b) Social and Cultural Benefits: Explore the social and cultural dimensions of agroforestry, including community empowerment, knowledge sharing, and the preservation of traditional practices. Understand how agroforestry fosters social cohesion, strengthens cultural identity, and creates a sense of pride and ownership among communities.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry stands as a beacon of hope in the face of land degradation, offering a transformative pathway from degradation to regeneration. Through its comprehensive benefits in soil restoration, biodiversity enhancement, climate resilience, and sustainable livelihoods, agroforestry proves to be a powerful tool for rehabilitating degraded lands and nurturing thriving ecosystems. Let us embrace the potential of agroforestry and work together to restore our planet, ensuring a sustainable and prosperous future for generations to come.