Empowering Farmers: Supporting Local Communities through Agroforestry
Discover how agroforestry can empower farmers and uplift local communities. This blog post explores the benefits of agroforestry investment in generating income, promoting sustainable agriculture, fostering resilience, and creating opportunities for tax-free retirement income. Learn how agroforestry can transform the lives of farmers and contribute to the overall development of local communities.
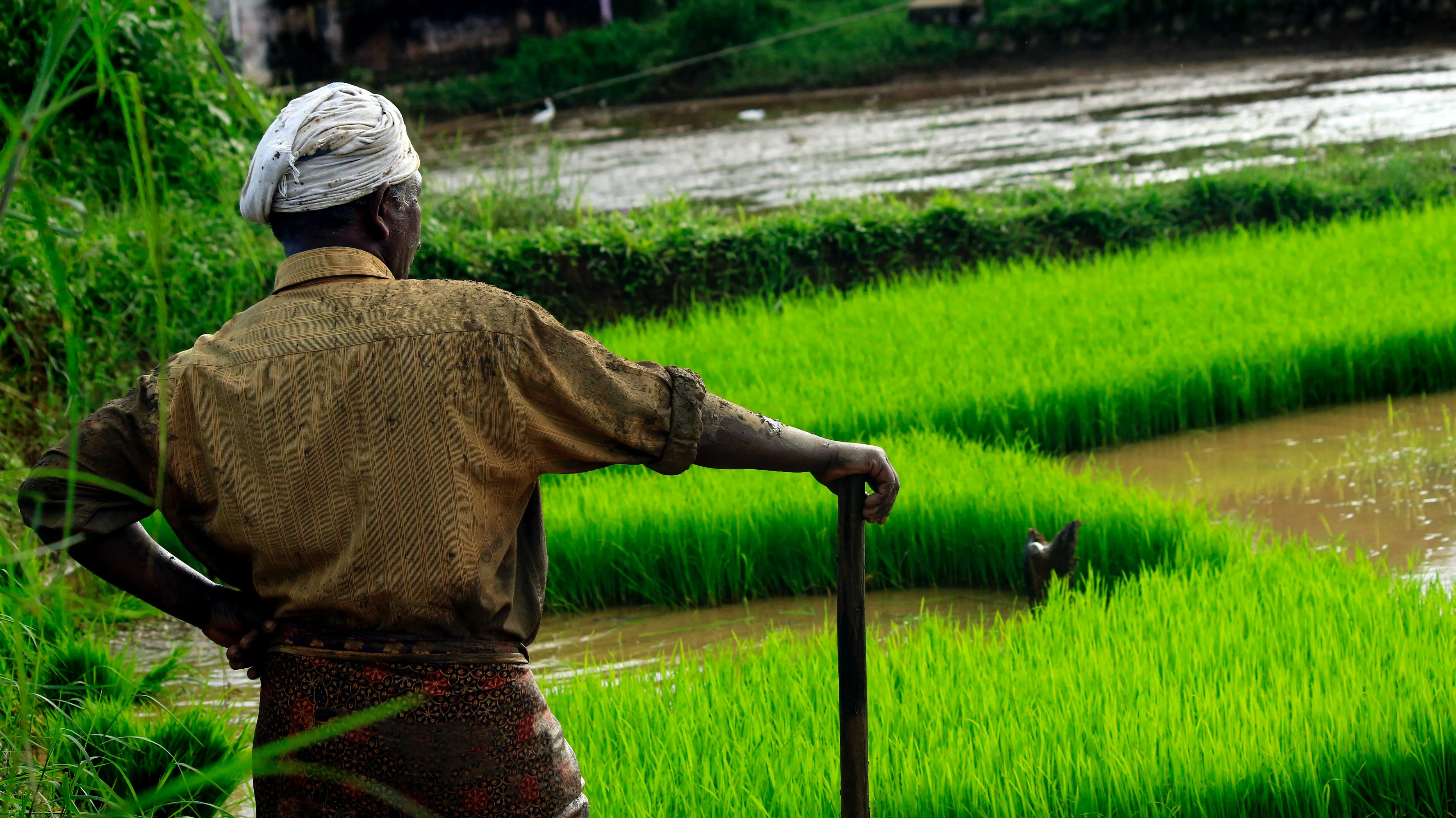

Introduction:
In a world where agricultural practices are constantly evolving, agroforestry has emerged as a powerful and sustainable approach that not only benefits the environment but also empowers farmers and supports local communities. Agroforestry integrates trees, crops, and livestock in a harmonious and mutually beneficial system. Beyond its ecological advantages, agroforestry offers numerous socio-economic benefits, generating income, promoting sustainable agriculture, fostering resilience, and even creating opportunities for tax-free retirement income. In this blog post, we will delve into the ways agroforestry empowers farmers and supports local communities, highlighting the transformative potential of this practice.
1. Generating Income: A Sustainable Livelihood
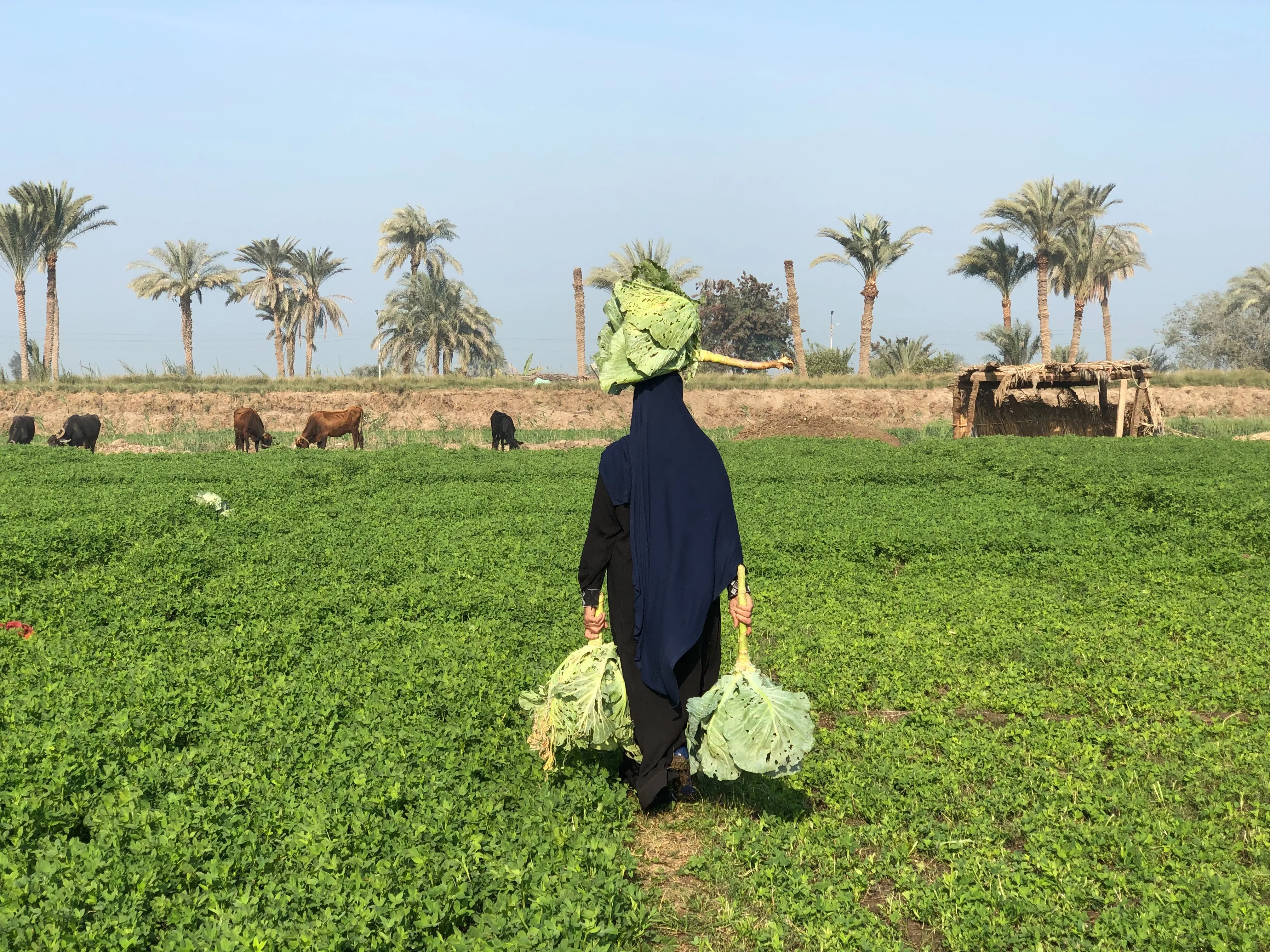
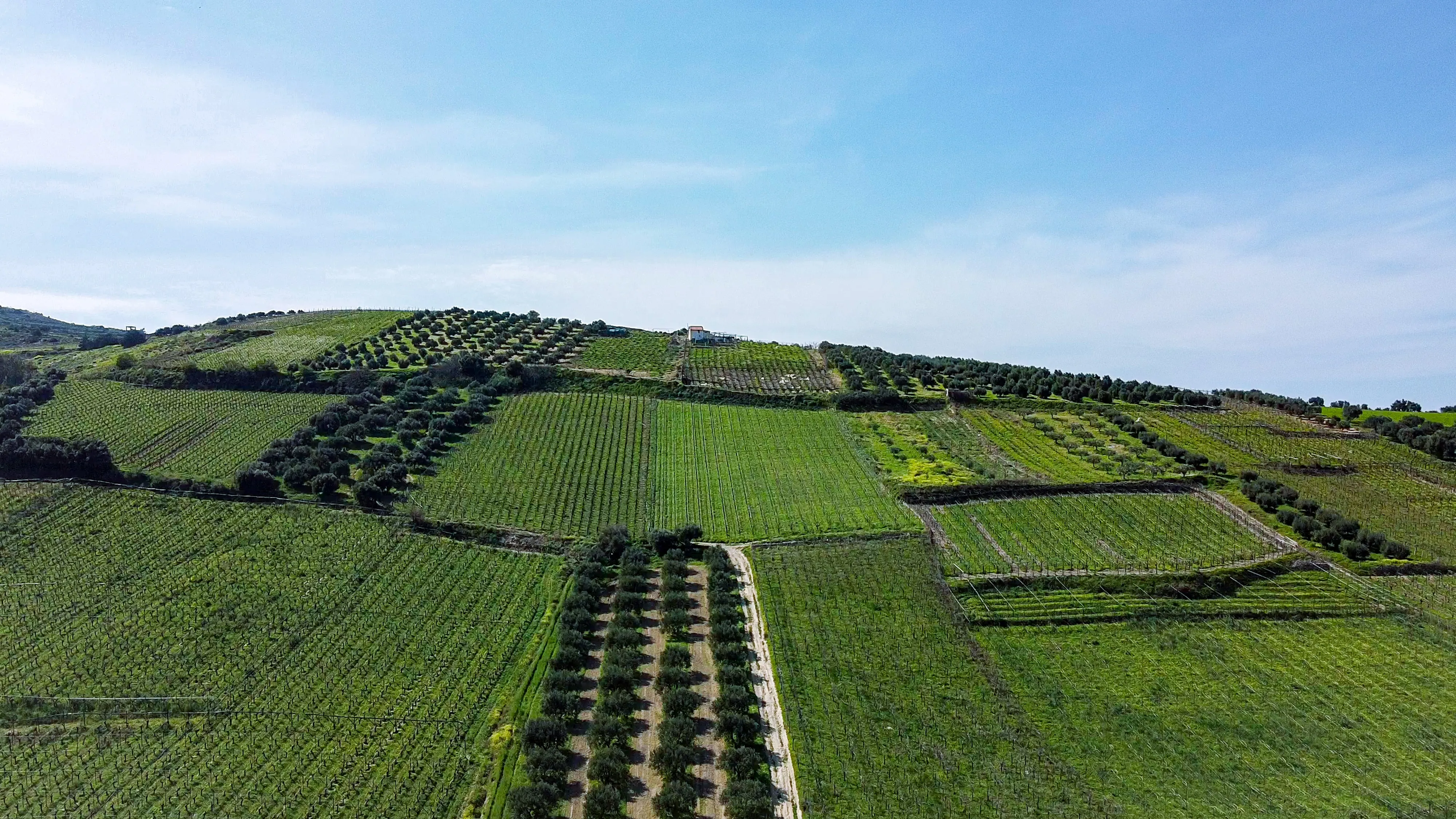
Agroforestry provides farmers with diversified income streams, reducing their reliance on a single crop or livestock. By incorporating a variety of trees, crops, and animals, agroforestry allows farmers to harness multiple revenue sources. Trees offer valuable products such as fruits, nuts, timber, and medicinal plants, while crops and livestock provide additional income streams. The combination of these diverse elements creates a resilient and sustainable livelihood, enabling farmers to earn a steady income throughout the year. Agroforestry also presents opportunities for value-added processing, such as producing and selling tree-based products or engaging in agro-tourism ventures. The economic benefits of agroforestry contribute to poverty reduction, economic stability, and improved living standards within local communities.
2. Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Environmental Stewardship
Agroforestry practices promote sustainable agriculture by enhancing soil fertility, conserving water resources, and reducing the need for chemical inputs. The presence of trees in agroforestry systems improves soil structure, prevents erosion, and enhances nutrient cycling. Trees also contribute to water conservation, reducing runoff and replenishing groundwater. This sustainable approach to agriculture safeguards the long-term productivity of farmland, enabling farmers to cultivate their land for generations to come. By adopting agroforestry practices, farmers become environmental stewards, preserving natural resources and mitigating the impacts of climate change. The sustainability of agroforestry practices not only benefits farmers but also ensures the resilience and well-being of the entire community.
3. Fostering Resilience: Climate Change Adaptation
As climate change continues to pose challenges to agricultural systems, agroforestry emerges as a resilient solution. The diverse composition of agroforestry systems provides inherent resilience to climatic variations, extreme weather events, and pest outbreaks. The shade provided by trees protects crops and livestock from heat stress, while the root systems of trees help improve water infiltration and reduce the risk of flooding. Agroforestry acts as a natural insurance policy, buffering farmers against the uncertainties of a changing climate. By adopting agroforestry practices, farmers can adapt and thrive in the face of climate-related challenges, ensuring the long-term sustainability of their agricultural activities.
4. Creating Opportunities for Tax-Free Retirement Income
Agroforestry investments offer a unique advantage for farmers seeking tax-free retirement income. In many countries, income generated from agriculture, including agroforestry, may be exempt from taxation. By strategically investing in agroforestry, farmers can secure a reliable source of tax-free retirement income. The long-term nature of agroforestry projects aligns well with retirement planning, as trees take time to mature and generate substantial returns. Agroforestry investment provides farmers with a sustainable and tax-efficient way to build wealth and secure their financial future, allowing them to enjoy the fruits of their labor during retirement.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry is not just a sustainable agricultural practice; it is a catalyst for empowering farmers and supporting local communities. Through diversified income streams, sustainable agriculture practices, climate change adaptation, and opportunities for tax-free retirement income, agroforestry uplifts farmers and promotes the overall development of local communities. By embracing agroforestry, we can create a more resilient and prosperous future, where farmers thrive, ecosystems flourish, and communities prosper. Let us harness the power of agroforestry to empower farmers and build sustainable, inclusive, and vibrant communities.