Cooperative Greenery: The Role of Community in Agroforestry Investment
Discover the power of community-driven Agroforestry investments and their potential for financial growth, tax savings, and tax-free retirement income. Explore how investing in cooperative Agroforestry projects empowers communities, promotes sustainability, and offers a rewarding and impactful investment opportunity.

Introduction:
Agroforestry investments take on a new dimension when community-driven approaches are embraced. This article delves into the significant role of community participation in Agroforestry investments and highlights the benefits of this cooperative model. By examining the cooperative greenery of community-based Agroforestry projects, investors can unlock opportunities for financial growth while making a positive impact on society and the environment.
1. Empowering Communities:
1.1 Shared Decision-Making: In community-driven Agroforestry investments, community members actively participate in decision-making processes, ensuring their voices are heard, and their needs are met. This participatory approach strengthens community cohesion and enhances project outcomes.
1.2 Local Resource Management: Community involvement empowers local residents to manage and protect natural resources, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility. Through sustainable land management practices, communities can ensure the longevity of Agroforestry systems and the preservation of local ecosystems.
1.3 Economic Empowerment: By engaging in Agroforestry projects, communities gain access to income-generating opportunities, job creation, and skill development. This economic empowerment improves livelihoods, reduces poverty, and enhances overall community well-being.
2. Sustainable Livelihoods:
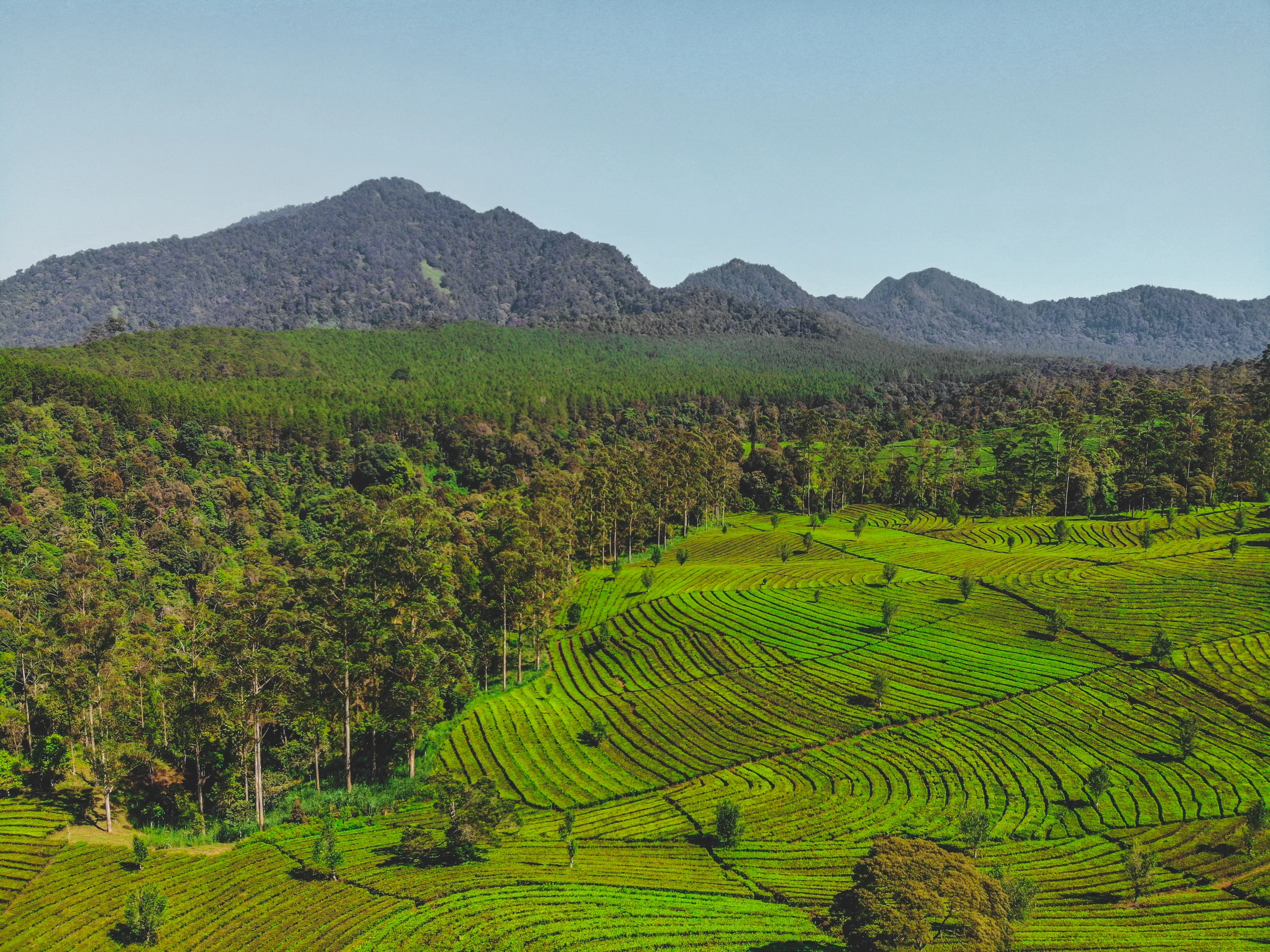
2.1 Diversified Income Streams: Agroforestry projects integrate tree cultivation with agriculture, providing communities with multiple income sources from timber, non-timber forest products, and agricultural crops. This diversification strengthens economic resilience, reducing dependency on single commodities and enhancing income stability.
2.2 Economic Resilience: The diversification of income streams reduces vulnerability to market fluctuations, creating more resilient local economies. Agroforestry investments offer long-term financial stability by providing a steady flow of revenue from various products and services.
2.3 Food Security: Agroforestry systems contribute to food security by enhancing agricultural productivity, increasing crop diversity, and improving nutrition. Community-based Agroforestry projects ensure sustainable food production, reducing reliance on external food sources and strengthening local food systems.
3. Environmental Stewardship:
3.1 Ecosystem Restoration: Community-driven Agroforestry investments promote ecological balance by restoring degraded lands, conserving biodiversity, and mitigating climate change impacts. Through reforestation and agroecological practices, Agroforestry projects contribute to ecosystem restoration and provide critical habitat for wildlife.
3.2 Sustainable Land Management: By combining trees with agricultural practices, Agroforestry projects improve soil health, reduce erosion, and enhance water management. This sustainable land management approach preserves soil fertility, minimizes the use of chemical inputs, and protects water resources.
3.3 Carbon Sequestration: Agroforestry systems play a crucial role in sequestering carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts. The integration of trees in Agroforestry projects helps capture and store carbon, offsetting greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
4. Tax Benefits and Social Impact:
4.1 Tax Savings: Depending on the jurisdiction, investors in community-based Agroforestry projects may be eligible for tax deductions or credits related to Agroforestry investments, leading to potential tax savings. These incentives further enhance the financial attractiveness of Agroforestry investments.
4.2 Social Impact: Community-based Agroforestry investments have far-reaching social benefits, including poverty reduction, community resilience, and the preservation of cultural heritage. By investing in projects that prioritize social impact, investors can make a meaningful contribution to local communities and promote social equity.
Conclusion:
Cooperative Agroforestry investments driven by community involvement offer investors a unique opportunity to achieve financial success while making a positive impact on society and the environment. By empowering communities, building sustainable livelihoods, promoting environmental stewardship, and leveraging tax benefits, investors can contribute to a more equitable and sustainable future. Embrace the cooperative greenery of community-based Agroforestry investments and be part of the transformation towards a prosperous, inclusive, and environmentally conscious world.