Climate Resilience and Agroforestry: An Overview
Explore the intersection of climate resilience and agroforestry. Discover the benefits of agroforestry investments, including tax savings and the potential for tax-free retirement income. Gain insights into how agroforestry practices enhance climate resilience and contribute to a sustainable future.

Introduction:
As the world grapples with the escalating challenges posed by climate change, the need for climate resilience becomes paramount. In the agricultural sector, where climate impacts can jeopardize food security and livelihoods, agroforestry emerges as a powerful solution. By integrating trees into agricultural systems, agroforestry fosters climate resilience while offering numerous environmental, economic, and social benefits. In this blog post, we will explore the dynamic relationship between climate resilience and agroforestry, highlighting the transformative potential of this practice and the opportunities it provides through investments, tax savings, and tax-free retirement income.
1. Understanding Agroforestry:
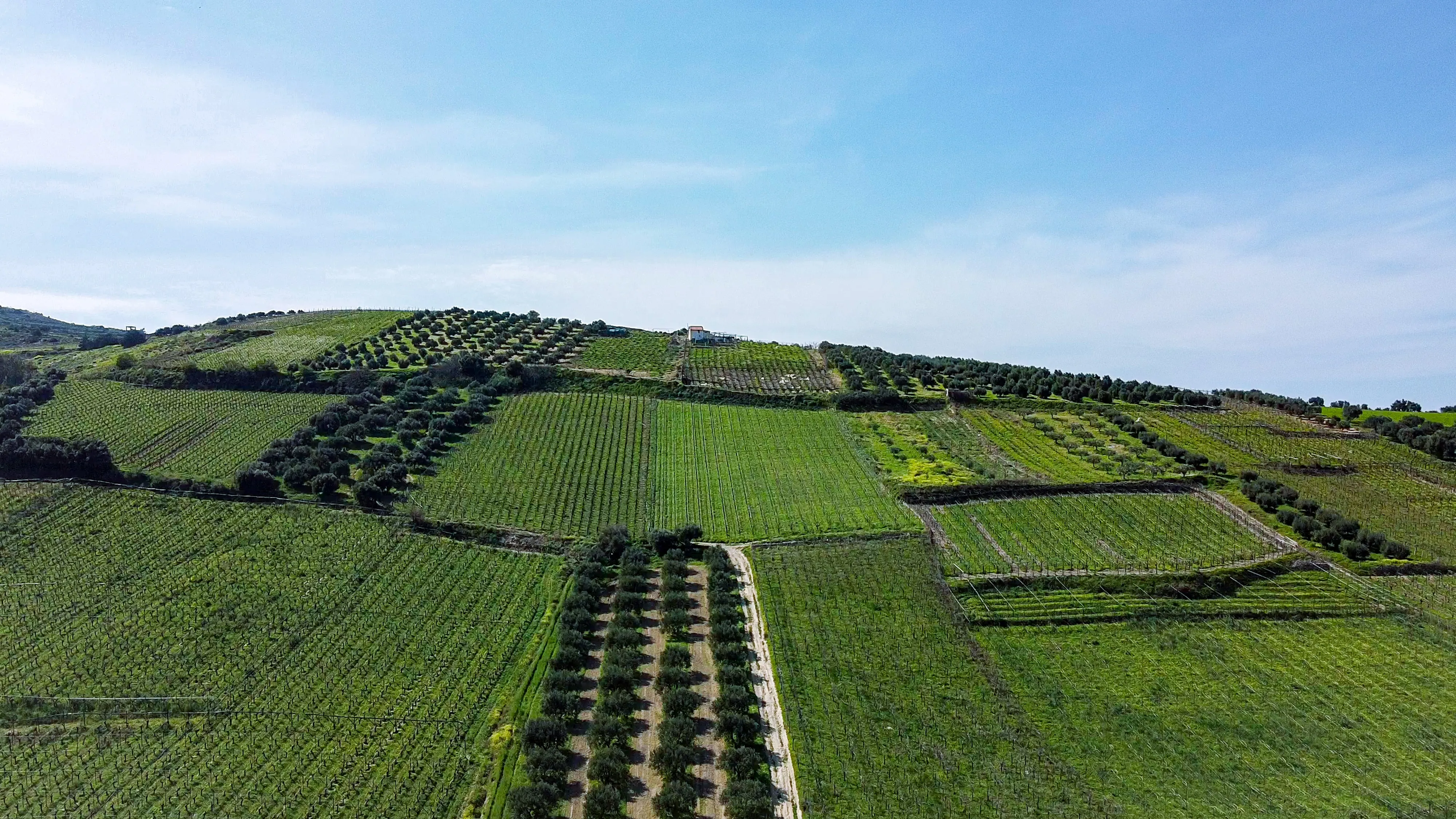
Agroforestry is a sustainable land management approach that combines agriculture and forestry, integrating trees with crops or livestock. This system harnesses the synergy between different plant species, creating mutually beneficial relationships that enhance productivity, biodiversity, and resilience.
2. Climate Resilience and Agroforestry:
Agroforestry practices contribute to climate resilience in several ways:
a) Enhanced Adaptation: Agroforestry systems help farmers adapt to climate variability and extreme weather events. The presence of trees provides shade, mitigating heat stress for crops and livestock. Trees also act as windbreaks, protecting against strong winds and reducing soil erosion. These adaptations support agricultural productivity and minimize the impact of climate-related challenges.
b) Soil Health and Water Management: Agroforestry enhances soil health and water management, critical aspects of climate resilience. Trees' deep root systems improve soil structure, prevent erosion, and enhance water infiltration, thus reducing runoff and increasing water availability for crops during dry periods. This efficient water management contributes to the sustainability of farming practices.
c) Carbon Sequestration: Agroforestry plays a significant role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Trees store carbon in their biomass and the soil, offsetting greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to climate change adaptation efforts. Agroforestry systems act as carbon sinks, promoting carbon sequestration and reducing the impact of climate change.
3. Agroforestry as an Investment:
Agroforestry investments offer multiple benefits, aligning financial returns with environmental and social impact:
a) Long-Term Returns: Agroforestry investments provide long-term financial rewards. While trees require time to mature, they generate income through timber, fruits, nuts, or other tree-based products. Patient investors can benefit from stable and lucrative returns as the trees reach maturity.
b) Tax Savings and Incentives: Governments often provide tax incentives for agroforestry investments due to their environmental benefits. These incentives can include tax deductions for establishing agroforestry systems or reduced tax rates on income generated from agroforestry operations. Leveraging these incentives can lead to significant tax savings.
c) Tax-Free Retirement Income: Agroforestry investments offer a unique opportunity for tax-free retirement income. As trees mature and generate revenue, the income can supplement retirement funds without incurring income tax. This tax-free income provides financial security and stability for retirees.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry stands as a vital tool in promoting climate resilience, offering a multifaceted approach that enhances adaptation, soil health, water management, and carbon sequestration. Moreover, agroforestry investments present an opportunity to align financial returns with environmental stewardship, with potential tax savings and tax-free retirement income. By embracing agroforestry, we can foster climate resilience, support sustainable agricultural practices, and pave the way for a more secure and sustainable future.