Climate Control: Agroforestry's Effect on Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Discover how agroforestry, a sustainable land-use practice, can have a profound impact on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This informative blog post explores the concept of agroforestry and its effectiveness in mitigating climate change. It also highlights the potential for agroforestry investments, including tax savings and opportunities for tax-free retirement income, making it a smart choice for the environment and your financial future.

Introduction:
Climate change has become one of the most pressing challenges of our time, with greenhouse gas emissions playing a significant role in its acceleration. As the world seeks sustainable solutions, agroforestry has emerged as a powerful tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of agroforestry and explore its profound effect on mitigating climate change. We will also discuss the exciting potential for agroforestry investments, including tax savings and opportunities for tax-free retirement income, making it a wise choice for both the environment and your financial well-being.
1. Understanding Agroforestry:
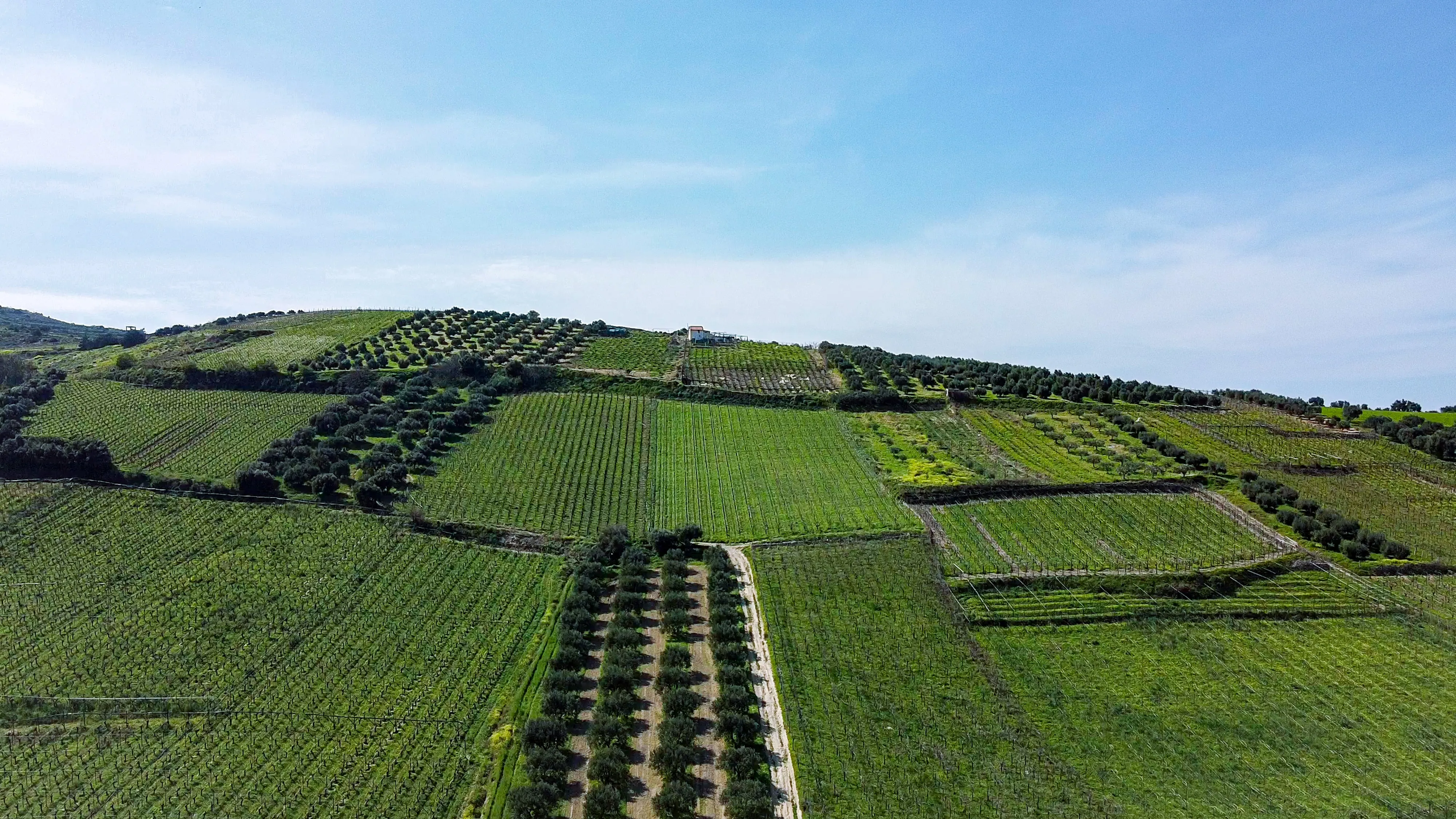
Agroforestry is a land-use system that integrates trees, crops, and/or livestock on the same piece of land. By combining agriculture and forestry, agroforestry promotes sustainability and environmental harmony.
2. Agroforestry's Impact on Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
a) Carbon Sequestration: Trees, known as nature's carbon sinks, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. Agroforestry systems, with their abundant tree cover, significantly contribute to carbon sequestration, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
b) Reduced Emissions from Land Use Change: Agroforestry minimizes the need for deforestation or land conversion for agricultural purposes. By utilizing existing land and integrating trees, agroforestry helps to prevent additional greenhouse gas emissions associated with land use change.
3. Environmental Benefits of Agroforestry:
a) Improved Soil Health: Agroforestry practices enhance soil fertility and structure, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and minimizing soil erosion. Healthy soils sequester more carbon and contribute to overall ecosystem resilience.
b) Biodiversity Conservation: Agroforestry systems provide habitats for diverse plant and animal species, promoting biodiversity conservation. This, in turn, enhances ecosystem resilience and contributes to long-term climate change adaptation.
4. Agroforestry Investments: Environmental and Financial Returns:
a) Tax Savings: Agroforestry investments often come with tax benefits. Depending on the jurisdiction, there may be incentives for tree planting and maintenance, resulting in potential tax savings. These incentives enhance the financial viability of agroforestry projects.
b) Tax-Free Retirement Income: Agroforestry investments offer a unique opportunity for tax-free retirement income. As trees mature, they can be selectively harvested, providing a renewable source of income during retirement. This tax-free income stream not only secures your financial future but also aligns with sustainable practices and greenhouse gas reduction efforts.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry stands as a powerful solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and addressing climate change. Through carbon sequestration, reduced land use change, and the promotion of soil health and biodiversity, agroforestry offers a multitude of environmental benefits. Moreover, agroforestry investments present an attractive opportunity for both environmental stewardship and financial gains, with potential tax savings and options for tax-free retirement income. By embracing agroforestry, we can actively contribute to climate control while securing a sustainable and prosperous future for ourselves and future generations.