Carbon Sequestration: How Agroforestry Helps
Explore the role of agroforestry in carbon sequestration and its potential to combat climate change. This blog post delves into the benefits of agroforestry in storing carbon dioxide, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting sustainable land management practices. Discover how agroforestry investments not only contribute to environmental conservation but also offer potential tax savings and opportunities for tax-free retirement income.

Introduction:
As concerns about climate change continue to escalate, finding effective solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions has become a global priority. Agroforestry, a sustainable land-use practice that integrates trees with agricultural systems, has gained recognition for its significant role in carbon sequestration. In this blog post, we delve into the concept of carbon sequestration and explore how agroforestry can help combat climate change by storing carbon dioxide. Additionally, we discuss the environmental benefits of agroforestry and highlight how it can provide potential tax savings and opportunities for tax-free retirement income through agroforestry investments.
1. Understanding Carbon Sequestration:
Carbon sequestration refers to the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, preventing its release into the environment. Trees play a crucial role in carbon sequestration through photosynthesis. They absorb carbon dioxide and convert it into organic matter, which is stored in their biomass and in the soil. Agroforestry enhances carbon sequestration by integrating trees with agricultural practices, effectively increasing the potential for carbon storage.
2. Agroforestry's Contribution to Carbon Sequestration:
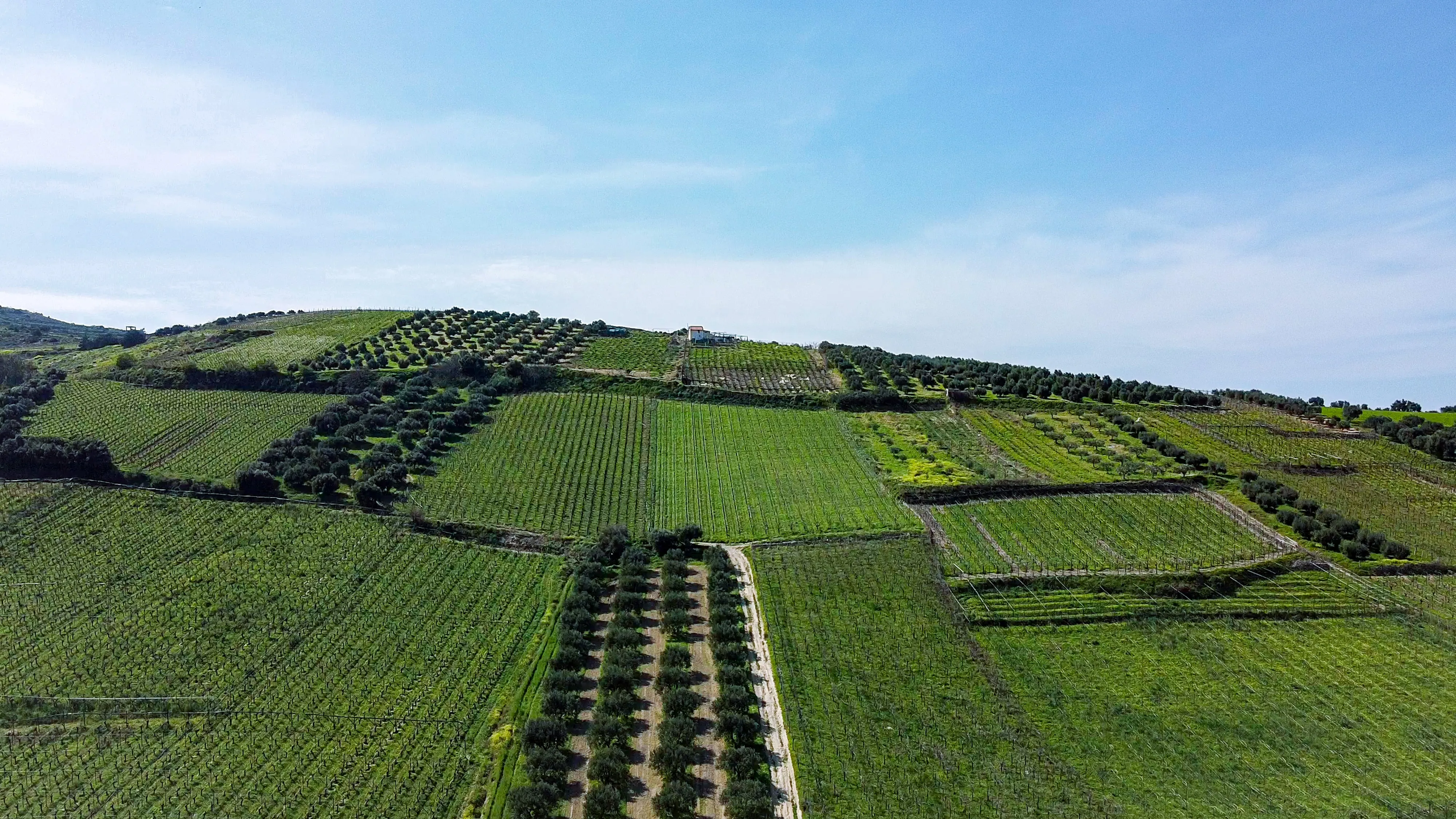
a) Tree Biomass: The presence of trees in agroforestry systems significantly enhances carbon sequestration. Trees are efficient at capturing carbon dioxide and storing it in their above-ground and below-ground biomass. Agroforestry practices that involve the cultivation of tree crops or the intercropping of trees with agricultural crops contribute to the accumulation of carbon in the form of woody biomass.
b) Soil Organic Carbon: Agroforestry also promotes the accumulation of soil organic carbon. The integration of trees with agricultural crops increases the organic matter content in the soil, which results in enhanced carbon storage. Tree leaves, branches, and root systems contribute to the organic matter input, fostering a favorable environment for soil microorganisms that facilitate carbon sequestration.
3. Climate Change Mitigation:
Agroforestry's contribution to carbon sequestration has significant implications for climate change mitigation. By storing carbon dioxide, agroforestry helps reduce greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of global warming. The integration of trees with agricultural systems also enhances ecosystem resilience, making agroforestry a valuable tool in adapting to climate change.
4. Environmental Benefits of Agroforestry:
a) Biodiversity Conservation: Agroforestry systems support diverse habitats, promoting biodiversity conservation. The presence of trees provides shelter, food, and nesting sites for various plant and animal species. This rich biodiversity enhances ecosystem stability and resilience, contributing to the overall health of the environment.
b) Soil Health and Water Management: Agroforestry practices improve soil health by reducing erosion, enhancing water infiltration, and increasing water retention capacity. The tree canopy protects the soil from erosion caused by wind and water, while the root systems help retain moisture and prevent water runoff. These benefits support sustainable land management practices and contribute to environmental conservation.
5. Agroforestry Investments: Environmental and Financial Returns:
a) Tax Savings: Agroforestry investments offer potential tax savings through various mechanisms. Depending on local regulations, tax incentives may be available for agroforestry activities, such as deductions for tree planting and maintenance expenses. These tax savings can enhance the financial returns on agroforestry investments.
b) Tax-Free Retirement Income: Agroforestry investments can also provide opportunities for tax-free retirement income. As tree crops mature, they can be harvested and sold, offering a sustainable income source during retirement. This tax-free income stream offers financial security while contributing to carbon sequestration efforts.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry's ability to sequester carbon dioxide makes it a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. By integrating trees with agricultural practices, agroforestry enhances carbon storage, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and promotes sustainable land management. Moreover, agroforestry investments offer potential tax savings and opportunities for tax-free retirement income, providing financial benefits alongside environmental conservation. Let us recognize the potential of agroforestry in combatting climate change and strive towards a greener and more sustainable future.