Agroforestry: Sowing the Seeds of Food Security
Discover how agroforestry, with its unique blend of sustainable practices and investment potential, plays a crucial role in ensuring food security. Explore the benefits of agroforestry investments, including tax savings and tax-free retirement income, and witness how this innovative approach is sowing the seeds of a resilient and abundant food future.

In a world grappling with the challenges of a growing population, climate change, and environmental degradation, ensuring food security has become more critical than ever before. We need innovative solutions that not only increase agricultural productivity but also promote sustainability and resilience. Enter agroforestry, a revolutionary approach that harnesses the power of trees, crops, and livestock to sow the seeds of food security. In this blog post, we will explore the transformative potential of agroforestry and how it can address the pressing issue of food security. Join us on this journey as we uncover the myriad benefits of agroforestry investments and their role in shaping a sustainable and nourished future.
1. Diversifying Agricultural Systems:
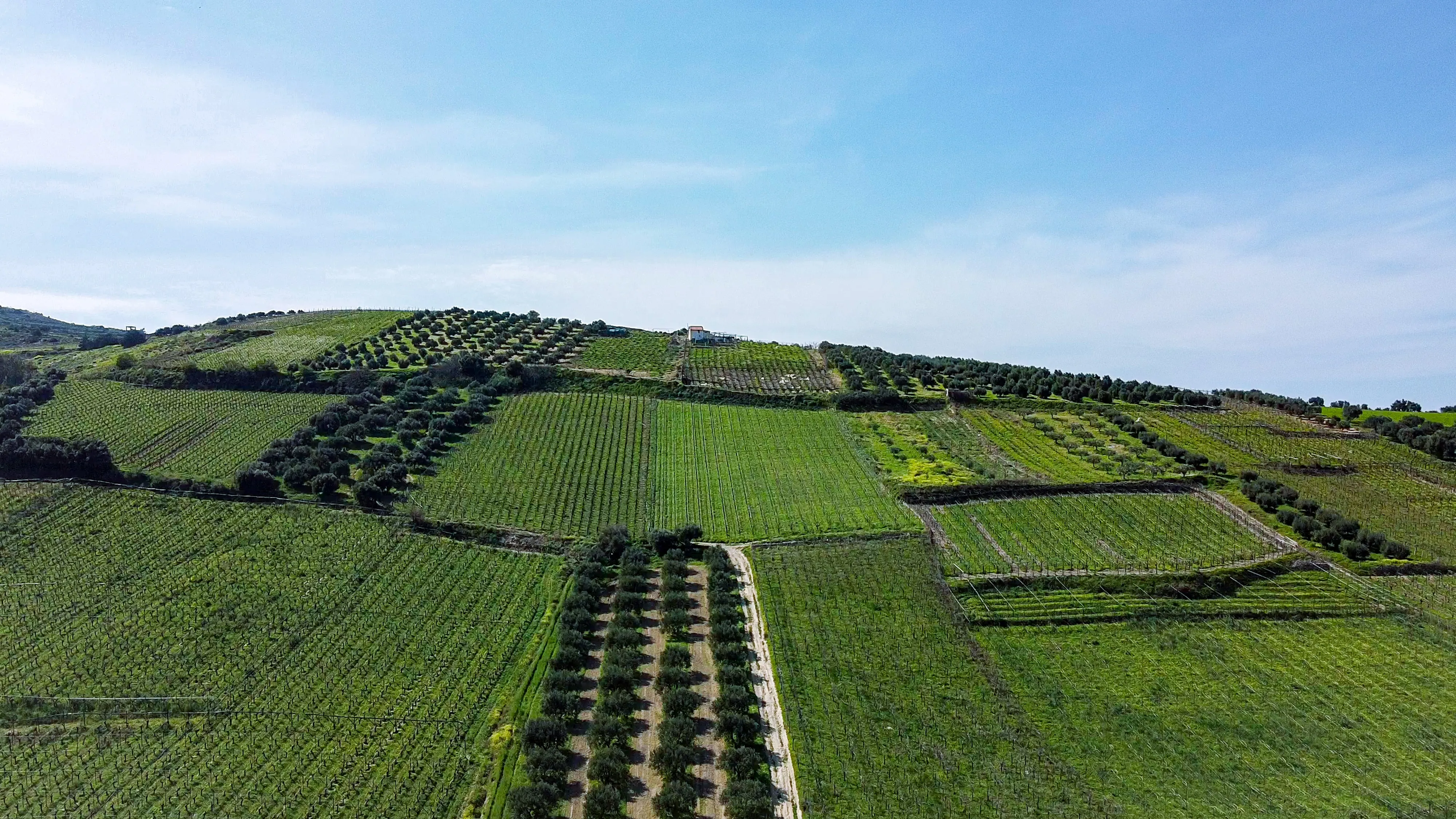
Agroforestry represents a departure from traditional monoculture farming practices by integrating trees, crops, and livestock in a mutually beneficial manner. This approach promotes biodiversity, reduces vulnerability to pests and diseases, and enhances ecosystem resilience. By diversifying agricultural systems, agroforestry not only safeguards against crop failures but also increases overall productivity and stability. The integration of tree species into farming landscapes provides additional sources of food, such as fruits and nuts, enriching the diet and improving nutrition.
2. Climate Change Resilience:
As climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, agroforestry emerges as a promising solution. The strategic planting of trees in agroforestry systems helps combat climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide, mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, and improving soil health. Trees act as natural windbreaks and shade providers, reducing water evaporation and preventing soil erosion. These climate-smart practices make agroforestry systems more resilient to extreme weather events, ensuring a stable food supply even in the face of climate uncertainties.
3. Enhancing Soil Fertility:
Agroforestry practices prioritize soil health and fertility through dynamic interactions between trees and other agricultural components. Trees contribute organic matter through fallen leaves, which enriches the soil and enhances its nutrient-holding capacity. Nitrogen-fixing tree species also play a crucial role in replenishing soil nutrients, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. The result is fertile soil that sustains long-term agricultural productivity and supports healthy crop growth, ultimately leading to increased food production.
4. Empowering Smallholder Farmers:
Agroforestry presents unique opportunities for smallholder farmers, who constitute a significant portion of the global food production system. By diversifying their income streams through agroforestry investments, farmers can reduce dependence on a single crop and increase financial stability. Agroforestry also promotes inclusive growth by empowering marginalized communities and fostering sustainable livelihoods. Through training and support, smallholder farmers can unlock the potential of agroforestry, improving their economic well-being and contributing to local food security.
5. Investment Potential:
Agroforestry investments offer not only environmental benefits but also financial rewards. By investing in agroforestry, individuals can enjoy tax savings and the potential for tax-free retirement income. The long-term nature of agroforestry projects aligns with retirement planning goals, providing a stable and sustainable source of income. Moreover, agroforestry investments offer the satisfaction of making a positive impact on food security and environmental sustainability, combining financial returns with social and environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, agroforestry represents a powerful solution to the pressing challenge of food security. By diversifying agricultural systems, enhancing climate resilience, improving soil fertility, empowering smallholder farmers, and offering attractive investment potential, agroforestry paves the way for a sustainable and nourished future. Let us sow the seeds of food security through agroforestry, nurturing the planet and ensuring a resilient and abundant food supply for generations to come.