Agroforestry and Soil Health: A Symbiotic Relationship
Explore the symbiotic relationship between agroforestry and soil health. Discover how agroforestry practices can enhance soil fertility, prevent erosion, and promote long-term sustainability for agricultural systems. Join the movement towards a greener and healthier future!

Introduction:
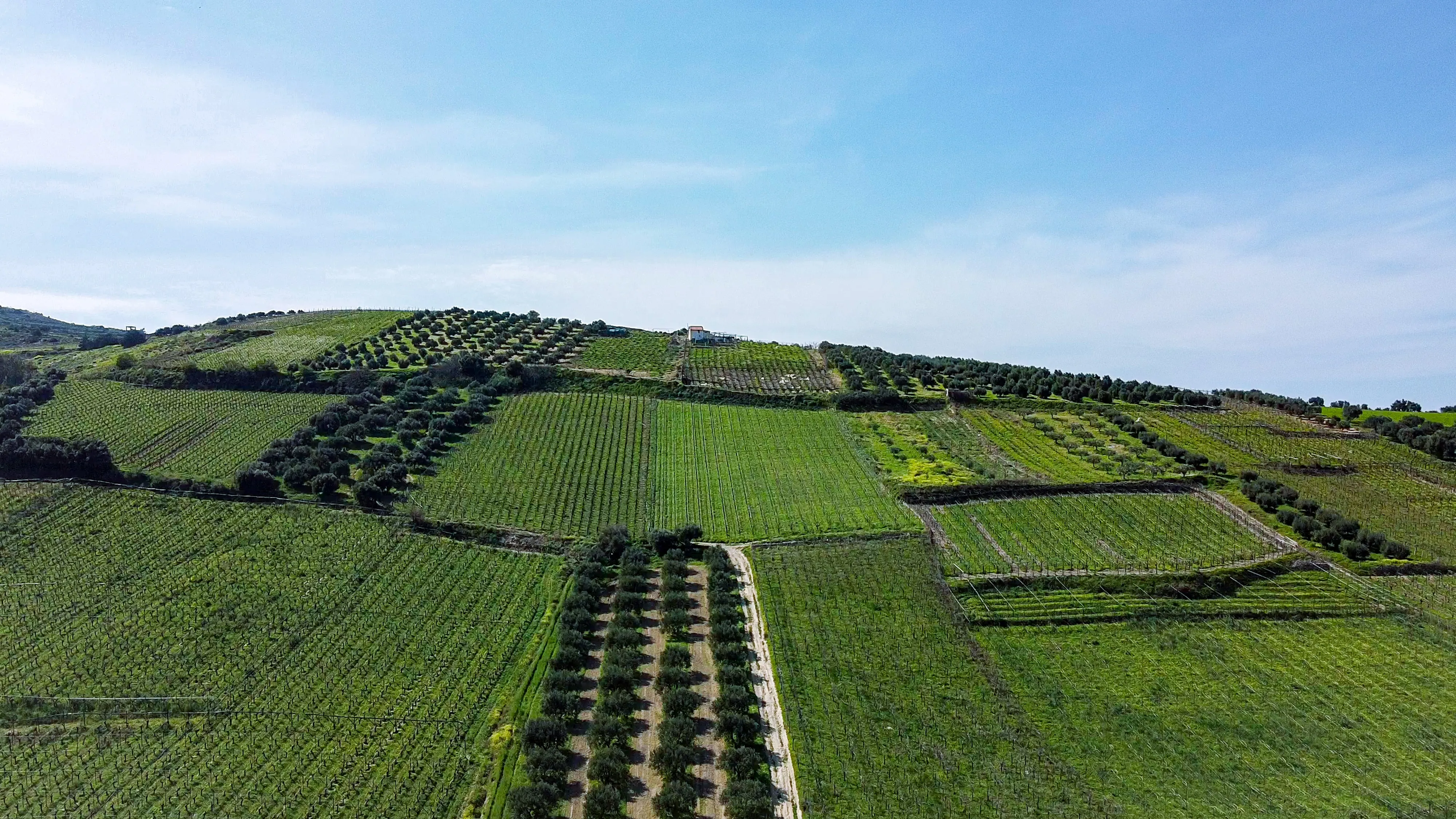
When it comes to sustainable land use practices, agroforestry stands out as a champion for both environmental conservation and agricultural productivity. One of the key benefits of agroforestry lies in its symbiotic relationship with soil health. By integrating trees with crops, agroforestry systems create a harmonious environment that enhances soil fertility, prevents erosion, and fosters long-term sustainability. In this blog post, we will explore the crucial connection between agroforestry and soil health, highlighting the ways in which this dynamic relationship can revolutionize agricultural systems. Join us on this enlightening journey towards a greener and healthier future!
1. Building Soil Fertility:
1.1 Nutrient Cycling: Agroforestry systems facilitate the cycling of nutrients between trees and crops. Tree roots tap into deep soil layers, accessing nutrients that may be out of reach for shallow-rooted crops. Through the natural process of nutrient transfer, trees enrich the soil, providing essential elements to support crop growth and productivity.
1.2 Organic Matter Accumulation: The presence of trees in agroforestry systems leads to increased organic matter accumulation in the soil. Fallen leaves, branches, and tree roots contribute to a rich and diverse soil organic matter content, improving soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient retention.
2. Preventing Soil Erosion:
2.1 Tree Canopy Protection: The presence of trees in agroforestry systems helps shield the soil from the impact of heavy rains and strong winds. The tree canopy acts as a natural shield, reducing the force of raindrops and wind gusts, thereby preventing soil erosion.
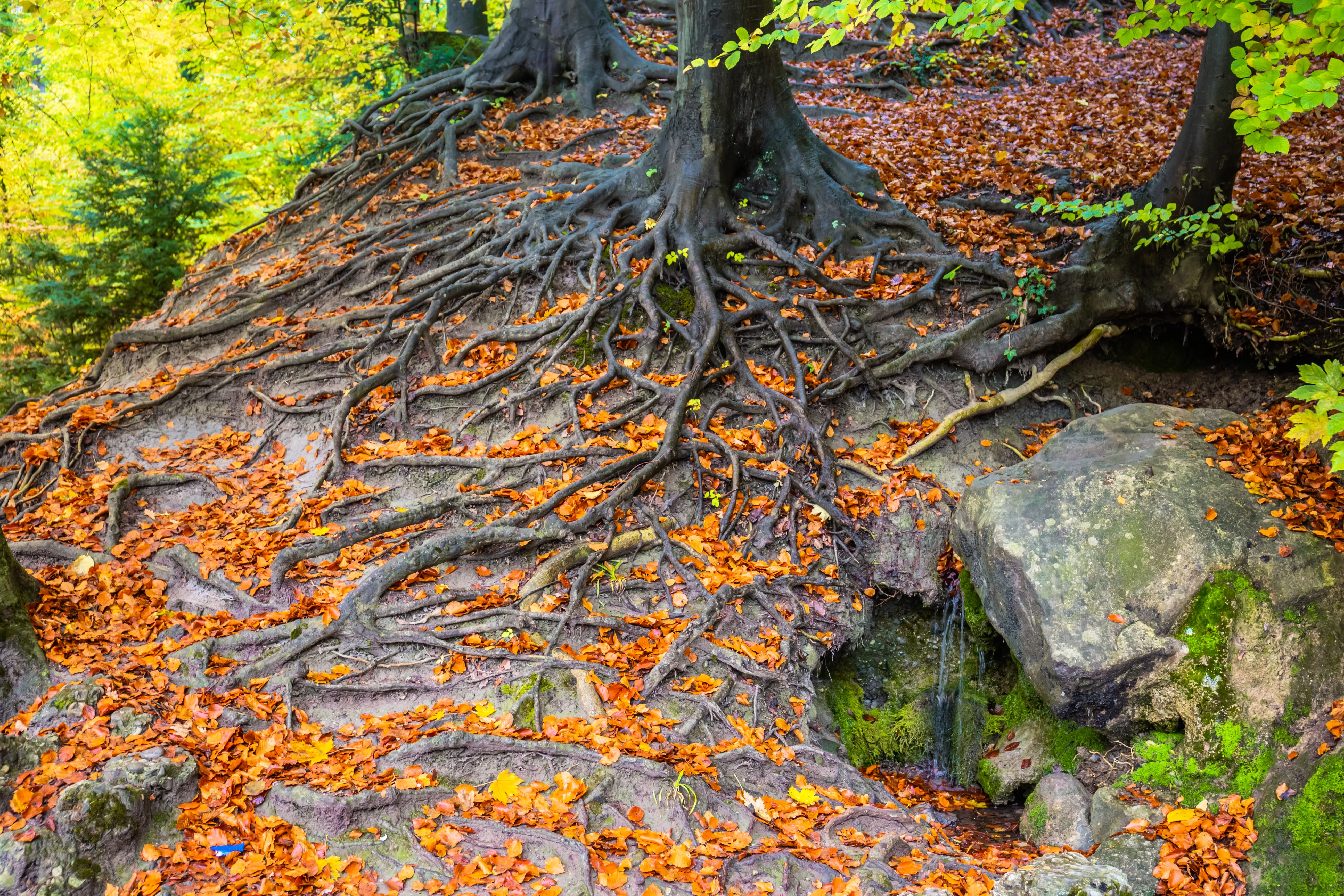
2.2 Root System Stability: Trees develop extensive root systems that bind and stabilize the soil, reducing the risk of erosion. The intricate network of tree roots acts as a barrier against water runoff, holding the soil in place even during periods of heavy rainfall.
3. Enhancing Water Management:
3.1 Water Infiltration: Agroforestry systems promote enhanced water infiltration into the soil. The tree canopy slows down rainfall, allowing water to penetrate gradually rather than running off the surface. This improves water retention capacity and reduces the risk of waterlogging or drought.
3.2 Water Use Efficiency: Agroforestry practices optimize water use efficiency by reducing evaporation and transpiration. The tree canopy provides shade, reducing water loss from the soil surface and the crops' transpiration rate, ultimately conserving water resources.
4. Long-Term Sustainability:
4.1 Conservation of Soil Health: Agroforestry systems prioritize the preservation and improvement of soil health over the long term. By reducing erosion, enhancing fertility, and promoting organic matter accumulation, agroforestry contributes to sustainable soil management practices that support agricultural productivity and environmental resilience.
4.2 Biodiversity and Ecological Balance: Agroforestry's integration of diverse tree and crop species creates a habitat that encourages biodiversity. The presence of diverse plant species attracts beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife, contributing to ecological balance and reducing the need for chemical inputs.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry represents a powerful approach to sustainable land use, with its impact reaching far beyond agricultural productivity. Through its symbiotic relationship with soil health, agroforestry enhances fertility, prevents erosion, and promotes long-term sustainability. By embracing agroforestry practices, we can build resilient agricultural systems that prioritize both the health of the land and the prosperity of farmers. Join the movement towards a greener and healthier future, where agroforestry and soil health go hand in hand, nourishing the planet and ensuring a sustainable legacy for generations to come.