Adapting to Climate Change: Unlocking the Potential of Agroforestry
Explore the transformative potential of agroforestry as an investment option for climate change adaptation. Discover the benefits of agroforestry investments, including tax savings and the potential for tax-free retirement income. Uncover how agroforestry serves as a powerful strategy for resilience, sustainability, and long-term prosperity in the face of climate change.

Introduction:
As the impacts of climate change become increasingly apparent, the need for adaptive strategies in agriculture has never been more critical. Agroforestry stands out as a powerful approach that not only mitigates the effects of climate change but also offers a promising investment opportunity. By integrating trees into agricultural landscapes, agroforestry provides multifaceted benefits that enhance resilience, foster sustainability, and secure long-term prosperity. This article explores the transformative potential of agroforestry as an adaptation strategy in the face of climate change, highlighting its role as an investment option. We will delve into the benefits of agroforestry investments, including tax savings and the potential for tax-free retirement income, while emphasizing its profound impact on resilience, sustainability, and financial growth in the era of climate change.
1. Understanding Agroforestry:
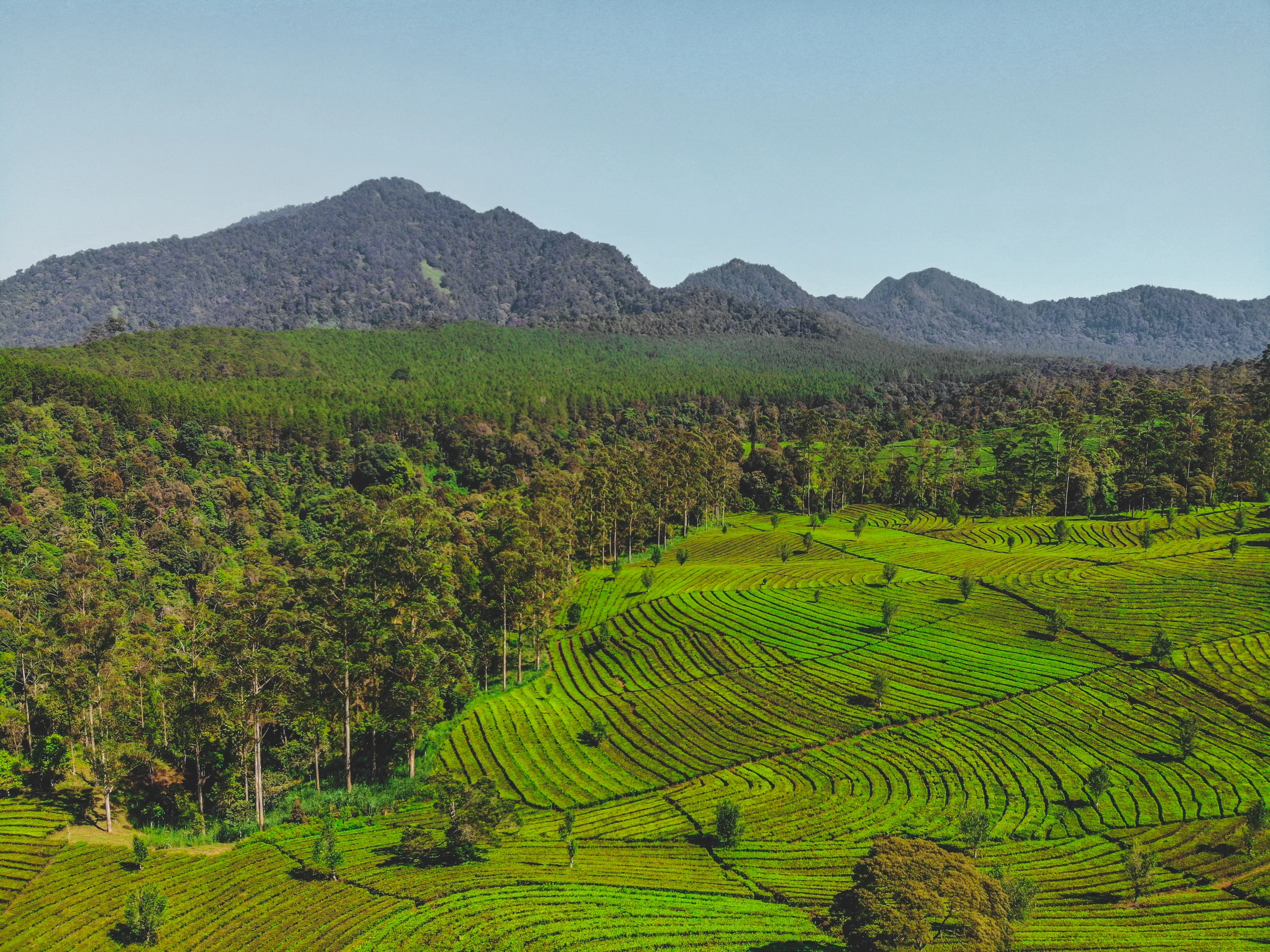
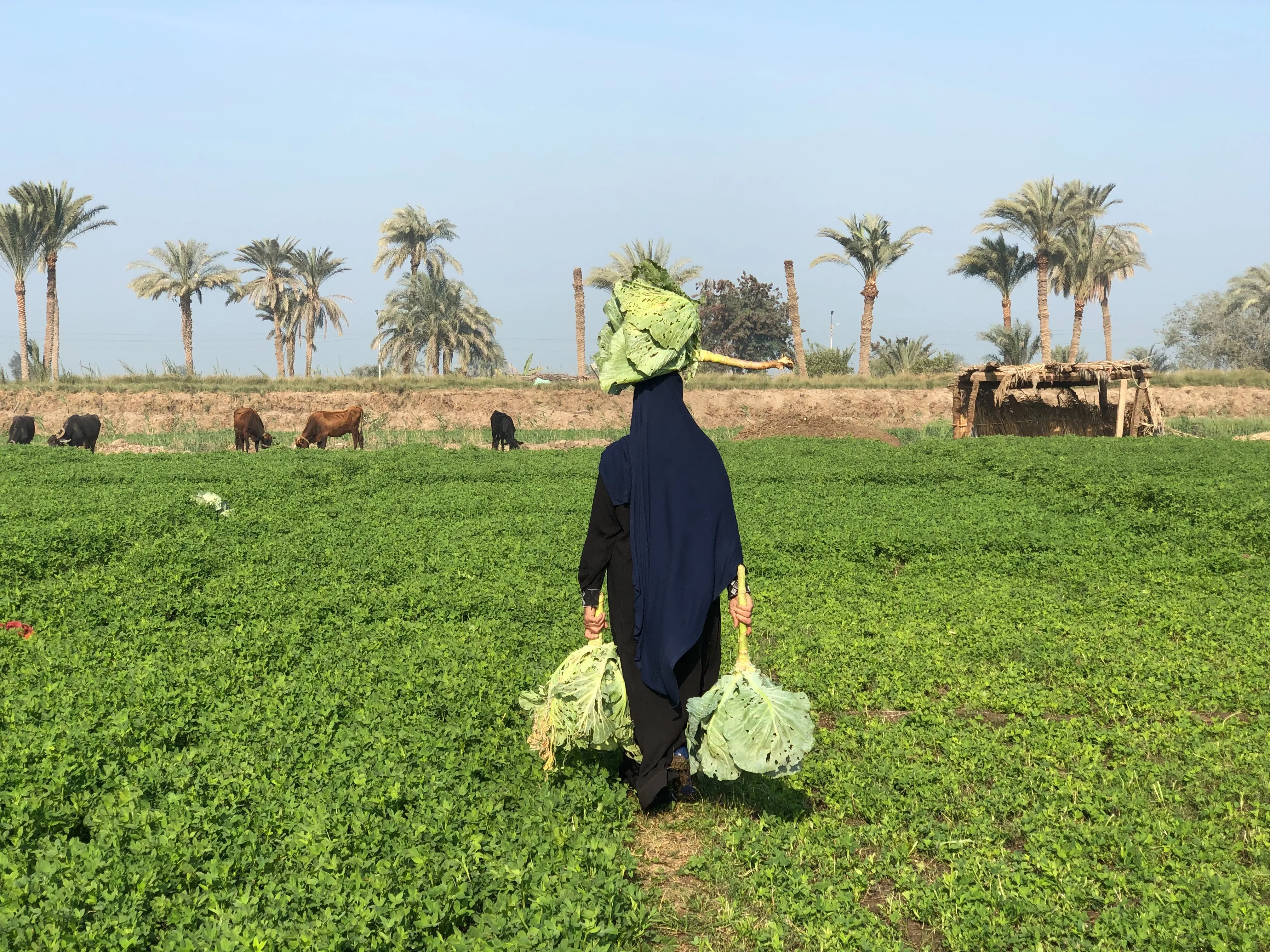
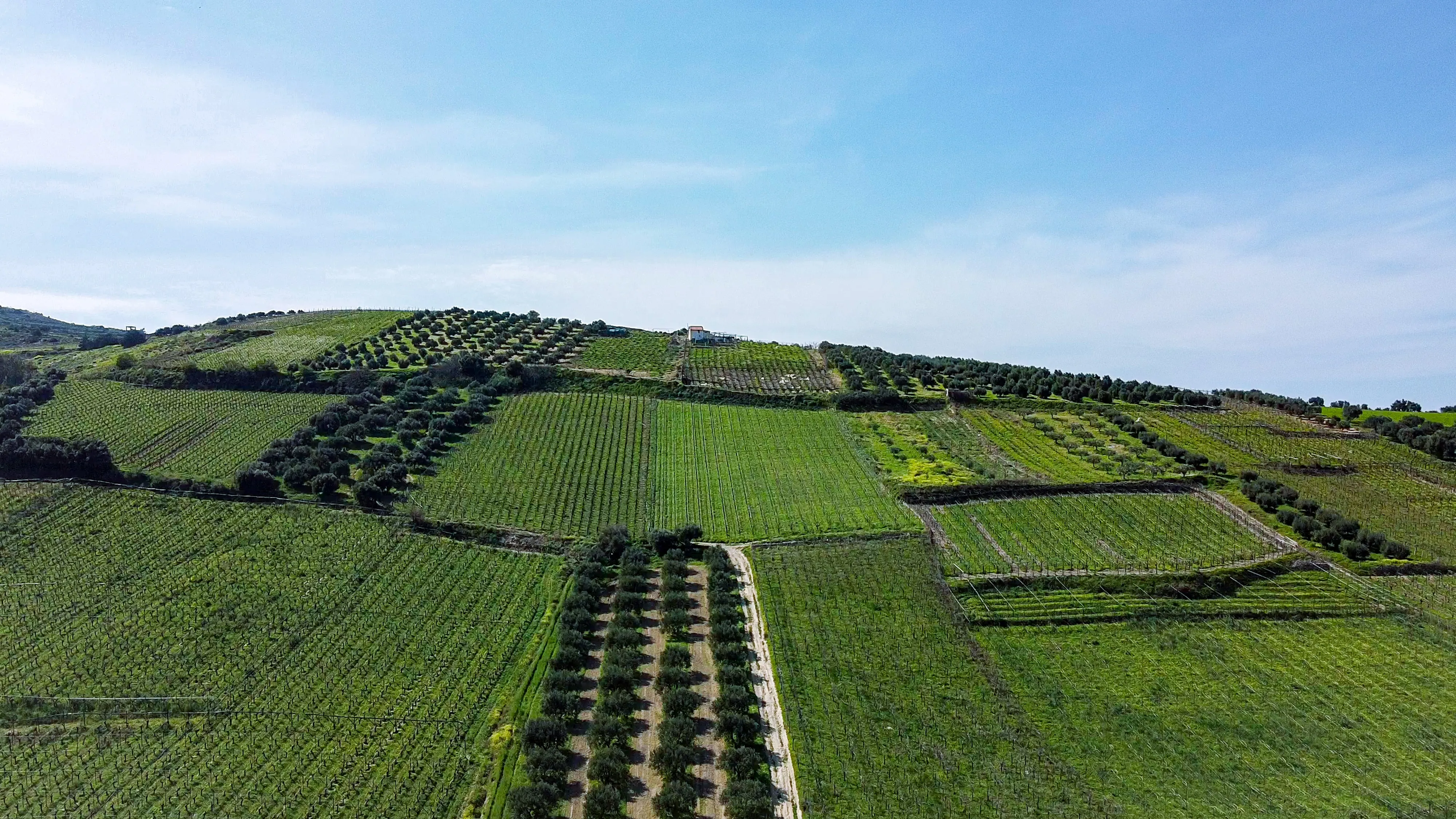
Agroforestry is a sustainable land management practice that combines agriculture and forestry, integrating trees with crops or livestock. This integrated approach leverages the power of ecological interactions, creating resilient and diverse systems that thrive in changing climatic conditions. Agroforestry offers a range of benefits for farmers, investors, and the environment.
2. Agroforestry as an Adaptation Strategy to Climate Change:
Agroforestry plays a vital role in adapting to climate change by providing the following benefits:
a) Climate Resilience: Agroforestry systems enhance climate resilience by diversifying the agricultural landscape. The presence of trees helps buffer against extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heatwaves. The shade provided by trees reduces soil temperature and evaporation rates, mitigating the risk of crop failure during heatwaves. Additionally, tree root systems improve soil structure, promoting water infiltration and reducing erosion.
b) Biodiversity Conservation: Agroforestry promotes biodiversity, creating habitats for a variety of plants, animals, and microorganisms. This diversity strengthens ecosystem resilience, supporting natural pest control, and enhancing pollination services. A biodiverse agroforestry system is more adaptable to changing climatic conditions, ensuring the continued productivity and sustainability of the agricultural landscape.
c) Carbon Sequestration and Climate Mitigation: Agroforestry contributes to climate change mitigation by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Trees in agroforestry systems capture and store significant amounts of carbon, helping to offset greenhouse gas emissions. By investing in agroforestry, individuals actively participate in climate change mitigation, supporting a more sustainable future.
3. Agroforestry Investments: A Pathway to Resilience and Financial Prosperity:
Agroforestry investments offer an opportunity for investors to align financial growth with climate resilience and sustainability:
a) Long-Term Financial Returns: Agroforestry investments provide long-term financial benefits. While trees take time to mature, they yield valuable products such as timber, fruits, nuts, or other tree-based commodities. Patient investors can enjoy stable and profitable returns as the trees reach maturity, providing a sustainable income source.
b) Tax Savings and Incentives: Agroforestry investments often come with tax benefits and incentives. Governments recognize the environmental benefits of agroforestry and may offer tax deductions for establishing agroforestry systems or reduced tax rates on income generated from agroforestry operations. Leveraging these incentives can lead to significant tax savings for investors.
c) Potential Tax-Free Retirement Income: Agroforestry investments offer a unique opportunity for tax-free retirement income. As trees mature and generate revenue, the income can supplement retirement funds without incurring income tax. This tax-free income provides financial security and stability during retirement.
Conclusion:
Agroforestry emerges as a transformative adaptation strategy in the face of climate change, offering benefits for farmers, investors, and the environment. By integrating trees into agricultural systems, agroforestry enhances climate resilience, biodiversity conservation, and carbon sequestration. Agroforestry investments provide long-term financial returns, tax savings, and potential tax-free retirement income, aligning financial prosperity with climate resilience and sustainability. Embracing agroforestry as an investment option not only contributes to climate change adaptation but also secures a prosperous and sustainable future.